Page 442 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 442
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 419 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch16_405-432.indd Page 419 9/3/10 6:19 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
Additional turn from Earth. A total of 12 Apollo astronauts walked on the Moon,
required to taking thousands of photographs, conducting hundreds of
show same side
to Earth experiments, and returning to Earth with over 380 kg (about
840 lb) of moon rocks (Table 16.1). In addition, instruments
Moon one were left on the Moon that continued to radio data back to
synodic month later
Earth after the Apollo program ended in 1972. As a result of
the Apollo missions, many questions were answered about the
Moon, but unanswered questions still remain.
Unmanned missions to the Moon have returned data about
mineral composition, topography, the presence of water, and
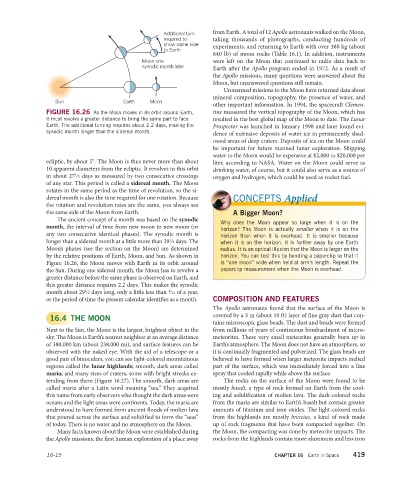
Sun Earth Moon
other important information. In 1994, the spacecraft Clemen-
FIGURE 16.26 As the Moon moves in its orbit around Earth, tine measured the vertical topography of the Moon, which has
it must revolve a greater distance to bring the same part to face resulted in the best global map of the Moon to date. The Lunar
Earth. The additional turning requires about 2.2 days, making the Prospector was launched in January 1998 and later found evi-
synodic month longer than the sidereal month.
dence of extensive deposits of water ice in permanently shad-
owed areas of deep craters. Deposits of ice on the Moon could
be important for future manned lunar exploration. Shipping
water to the Moon would be expensive at $2,000 to $20,000 per
ecliptic, by about 5°. The Moon is thus never more than about liter, according to NASA. Water on the Moon could serve as
10 apparent diameters from the ecliptic. It revolves in this orbit drinking water, of course, but it could also serve as a source of
1
in about 27 ⁄3 days as measured by two consecutive crossings oxygen and hydrogen, which could be used as rocket fuel.
of any star. This period is called a sidereal month. The Moon
rotates in the same period as the time of revolution, so the si-
dereal month is also the time required for one rotation. Because CONCEPTS Applied
the rotation and revolution rates are the same, you always see
the same side of the Moon from Earth. A Bigger Moon?
The ancient concept of a month was based on the synodic Why does the Moon appear so large when it is on the
month, the interval of time from new moon to new moon (or horizon? The Moon is actually smaller when it is on the
any two consecutive identical phases). The synodic month is horizon than when it is overhead. It is smaller because
longer than a sidereal month at a little more than 29 ⁄2 days. The when it is on the horizon, it is farther away by one Earth
1
Moon’s phases (see the section on the Moon) are determined radius. It is an optical illusion that the Moon is larger on the
by the relative positions of Earth, Moon, and Sun. As shown in horizon. You can test this by bending a paperclip so that it
Figure 16.26, the Moon moves with Earth in its orbit around is “one moon” wide when held at arm’s length. Repeat the
the Sun. During one sidereal month, the Moon has to revolve a paperclip measurement when the Moon is overhead.
greater distance before the same phase is observed on Earth, and
this greater distance requires 2.2 days. This makes the synodic
1
1
month about 29 ⁄2 days long, only a little less than ⁄12 of a year,
or the period of time the present calendar identifies as a month. COMPOSITION AND FEATURES
The Apollo astronauts found that the surface of the Moon is
covered by a 3 m (about 10 ft) layer of fine gray dust that con-
16.4 THE MOON
tains microscopic glass beads. The dust and beads were formed
Next to the Sun, the Moon is the largest, brightest object in the from millions of years of continuous bombardment of micro-
sky. The Moon is Earth’s nearest neighbor at an average distance meteorites. These very small meteorites generally burn up in
of 380,000 km (about 238,000 mi), and surface features can be Earth’s atmosphere. The Moon does not have an atmosphere, so
observed with the naked eye. With the aid of a telescope or a it is continually fragmented and pulverized. The glass beads are
good pair of binoculars, you can see light-colored mountainous believed to have formed when larger meteorite impacts melted
regions called the lunar highlands; smooth, dark areas called part of the surface, which was immediately forced into a fine
maria; and many sizes of craters, some with bright streaks ex- spray that cooled rapidly while above the surface.
tending from them (Figure 16.27). The smooth, dark areas are The rocks on the surface of the Moon were found to be
called maria after a Latin word meaning “sea.” They acquired mostly basalt, a type of rock formed on Earth from the cool-
this name from early observers who thought the dark areas were ing and solidification of molten lava. The dark-colored rocks
oceans and the light areas were continents. Today, the maria are from the maria are similar to Earth’s basalt but contain greater
understood to have formed from ancient floods of molten lava amounts of titanium and iron oxides. The light- colored rocks
that poured across the surface and solidified to form the “seas” from the highlands are mostly breccias, a kind of rock made
of today. There is no water and no atmosphere on the Moon. up of rock fragments that have been compacted together. On
Many facts known about the Moon were established during the Moon, the compacting was done by meteorite impacts. The
the Apollo missions, the first human exploration of a place away rocks from the highlands contain more aluminum and less iron
16-15 CHAPTER 16 Earth in Space 419