Page 578 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 578
/Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefile
tiL12214_ch22_541-564.indd Page 555 9/23/10 11:08 AM user-f465
tiL12214_ch22_541-564.indd Page 555 9/23/10 11:08 AM user-f465 /Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefiles
an equilibrium is reached between water vapor leaving the wick
45 and water vapor returning to the wick from the air. Since evapora-
tion lowers the temperature, the depression of the temperature of
40 the wet-bulb thermometer is an indirect measure of the water
vapor present in the air. The relative humidity can be determined
by obtaining the dry- and wet-bulb temperature readings and
35
referring to a relative humidity table such as the one found in
appendix C. If the humidity is 100 percent, no net evaporation will
Absolute humidity (g/m 3 ) 25 peratures will be the same. The lower the humidity, the greater the
30
take place from the wet bulb, and both wet- and dry-bulb tem-
difference in the temperature reading of the two thermometers.
You may have noticed that your hair becomes more or
less curly in humid weather. The human hair absorbs mois-
20
dry air. Since the change of length is proportional to changes
15 ture from the air, becoming longer in humid air and shorter in
in humidity, it is possible to use human hair to measure the
humidity. A hair hygrom eter is an instrument that measures
10 the humidity from changes in the length of hair. A bundle of
the hair is held under tension by a spring, and changes in the
5 length move a pointer on a dial that is calibrated to read the
relative humidity.
0
–20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50
CONCEPTS Applied
Temperature (°C)
Humidity Factors
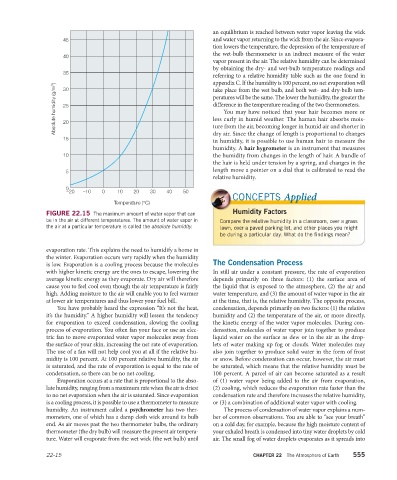
FIGURE 22.15 The maximum amount of water vapor that can
be in the air at different temperatures. The amount of water vapor in Compare the relative humidity in a classroom, over a grass
the air at a particular temperature is called the absolute humidity. lawn, over a paved parking lot, and other places you might
be during a particular day. What do the findings mean?
evaporation rate. This explains the need to humidify a home in
the winter. Evaporation occurs very rapidly when the humidity
is low. Evaporation is a cooling process because the molecules The Condensation Process
with higher kinetic energy are the ones to escape, lowering the In still air under a constant pressure, the rate of evaporation
average kinetic energy as they evaporate. Dry air will therefore depends primarily on three factors: (1) the surface area of
cause you to feel cool even though the air temperature is fairly the liquid that is exposed to the atmosphere, (2) the air and
high. Adding moisture to the air will enable you to feel warmer water temperature, and (3) the amount of water vapor in the air
at lower air temperatures and thus lower your fuel bill. at the time, that is, the relative humidity. The opposite process,
You have probably heard the expression “It’s not the heat, condensation, depends primarily on two factors: (1) the relative
it’s the humidity.” A higher humidity will lessen the tendency humidity and (2) the temperature of the air, or more directly,
for evaporation to exceed condensation, slowing the cooling the kinetic energy of the water vapor molecules. During con-
process of evaporation. You often fan your face or use an elec- densation, molecules of water vapor join together to produce
tric fan to move evaporated water vapor molecules away from liquid water on the surface as dew or in the air as the drop-
the surface of your skin, increasing the net rate of evaporation. lets of water making up fog or clouds. Water molecules may
The use of a fan will not help cool you at all if the relative hu- also join together to produce solid water in the form of frost
midity is 100 percent. At 100 percent relative humidity, the air or snow. Before condensation can occur, however, the air must
is saturated, and the rate of evaporation is equal to the rate of be saturated, which means that the relative humidity must be
condensation, so there can be no net cooling. 100 percent. A parcel of air can become saturated as a result
Evaporation occurs at a rate that is proportional to the abso- of (1) water vapor being added to the air from evaporation,
lute humidity, ranging from a maximum rate when the air is driest (2) cooling, which reduces the evaporation rate faster than the
to no net evaporation when the air is saturated. Since evaporation condensation rate and therefore increases the relative humidity,
is a cooling process, it is possible to use a thermometer to measure or (3) a combination of additional water vapor with cooling.
humidity. An instrument called a psychrometer has two ther- The process of condensation of water vapor explains a num-
mometers, one of which has a damp cloth wick around its bulb ber of common observations. You are able to “see your breath”
end. As air moves past the two thermometer bulbs, the ordinary on a cold day, for example, because the high moisture content of
thermometer (the dry bulb) will measure the present air tempera- your exhaled breath is condensed into tiny water droplets by cold
ture. Water will evaporate from the wet wick (the wet bulb) until air. The small fog of water droplets evaporates as it spreads into
22-15 CHAPTER 22 The Atmosphere of Earth 555