Page 606 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 606
/Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefiles
tiL12214_ch23_565-596.indd Page 583 9/23/10 11:07 AM user-f465
tiL12214_ch23_565-596.indd Page 583 9/23/10 11:07 AM user-f465 /Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefile
1,609 m (5,280 ft), and the altitude of St. Louis is 141 m (465 ft).
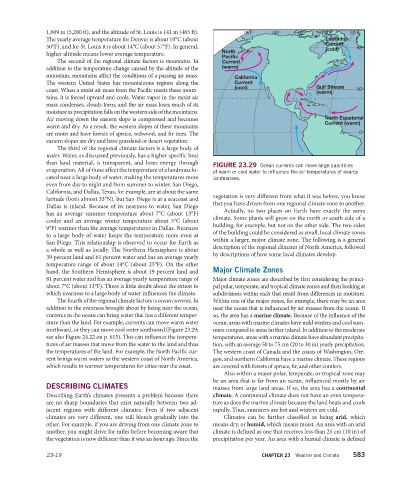
The yearly average temperature for Denver is about 10°C (about Labrador
Current
50°F), and for St. Louis it is about 14°C (about 57°F). In general, (cold)
higher altitude means lower average temperature. North
Pacific
The second of the regional climate factors is mountains. In Current
addition to the temperature change caused by the altitude of the (warm)
mountain, mountains affect the conditions of a passing air mass. California
The western United States has mountainous regions along the Current
(cool) Gulf Stream
coast. When a moist air mass from the Pacific meets these moun- (warm)
tains, it is forced upward and cools. Water vapor in the moist air
mass condenses, clouds form, and the air mass loses much of its
moisture as precipitation falls on the western side of the mountains.
Air moving down the eastern slope is compressed and becomes North Equatorial
Current (warm)
warm and dry. As a result, the western slopes of these mountains
are moist and have forests of spruce, redwood, and fir trees. The
eastern slopes are dry and have grassland or desert vegetation.
The third of the regional climate factors is a large body of
water. Water, as discussed previously, has a higher specific heat
than land material, is transparent, and loses energy through
FIGURE 23.29 Ocean currents can move large quantities
evaporation. All of these affect the temperature of a landmass lo- of warm or cool water to influence the air temperatures of nearby
cated near a large body of water, making the temperatures more landmasses.
even from day to night and from summer to winter. San Diego,
California, and Dallas, Texas, for example, are at about the same
vegetation is very different from what it was before, you know
latitude (both almost 33°N), but San Diego is at a seacoast and
that you have driven from one regional climate zone to another.
Dallas is inland. Because of its nearness to water, San Diego
Actually, no two places on Earth have exactly the same
has an average summer temperature about 7°C (about 13°F)
climate. Some plants will grow on the north or south side of a
cooler and an average winter temperature about 5°C (about
building, for example, but not on the other side. The two sides
9°F) warmer than the average temperatures in Dallas. Nearness
of the building could be considered as small, local climate zones
to a large body of water keeps the temperature more even at
within a larger, major climate zone. The following is a general
San Diego. This relationship is observed to occur for Earth as
description of the regional climates of North America, followed
a whole as well as locally. The Northern Hemisphere is about
by descriptions of how some local climates develop.
39 percent land and 61 percent water and has an average yearly
temperature range of about 14°C (about 25°F). On the other
hand, the Southern Hemisphere is about 19 percent land and Major Climate Zones
81 percent water and has an average yearly temperature range of Major climate zones are described by first considering the princi-
about 7°C (about 13°F). There is little doubt about the extent to pal polar, temperate, and tropical climate zones and then looking at
which nearness to a large body of water influences the climate. subdivisions within each that result from differences in moisture.
The fourth of the regional climate factors is ocean currents. In Within one of the major zones, for example, there may be an area
addition to the evenness brought about by being near the ocean, near the ocean that is influenced by air masses from the ocean. If
currents in the ocean can bring water that has a different temper- so, the area has a marine climate. Because of the influence of the
ature than the land. For example, currents can move warm water ocean, areas with marine climates have mild winters and cool sum-
northward, or they can move cool water southward (Figure 23.29; mers compared to areas farther inland. In addition to the moderate
see also Figure 24.22 on p. 615). This can influence the tempera- temperatures, areas with a marine climate have abundant precipita-
tures of air masses that move from the water to the land and thus tion, with an average 50 to 75 cm (20 to 30 in) yearly precipitation.
the temperatures of the land. For example, the North Pacific cur- The western coast of Canada and the coasts of Washington, Ore-
rent brings warm waters to the western coast of North America, gon, and northern California have a marine climate. These regions
which results in warmer temperatures for cities near the coast. are covered with forests of spruce, fir, and other conifers.
Also within a major polar, temperate, or tropical zone may
be an area that is far from an ocean, influenced mostly by air
DESCRIBING CLIMATES masses from large land areas. If so, the area has a continental
Describing Earth’s climates presents a problem because there climate. A continental climate does not have an even tempera-
are no sharp boundaries that exist naturally between two ad- ture as does the marine climate because the land heats and cools
jacent regions with different climates. Even if two adjacent rapidly. Thus, summers are hot and winters are cold.
climates are very different, one still blends gradually into the Climates can be further classified as being arid, which
other. For example, if you are driving from one climate zone to means dry, or humid, which means moist. An area with an arid
another, you might drive for miles before becoming aware that climate is defined as one that receives less than 25 cm (10 in) of
the vegetation is now different than it was an hour ago. Since the precipitation per year. An area with a humid climate is defined
23-19 CHAPTER 23 Weather and Climate 583