Page 35 - Ranger SPM 2022 - Science
P. 35
Science SPM Chapter 6 Electrochemistry
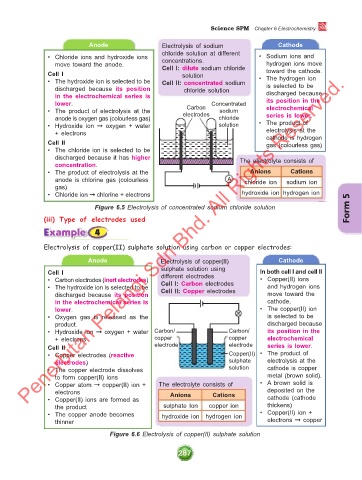
Anode Electrolysis of sodium Cathode
chloride solution at different
• Chloride ions and hydroxide ions concentrations. • Sodium ions and
move toward the anode. Cell I: dilute sodium chloride hydrogen ions move
Cell I solution toward the cathode.
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
• The hydroxide ion is selected to be Cell II: concentrated sodium • The hydrogen ion
discharged because its position chloride solution is selected to be
in the electrochemical series is discharged because
lower. Concentrated its position in the
Carbon
• The product of electrolysis at the electrodes sodium electrochemical
anode is oxygen gas (colourless gas) chloride series is lower.
• Hydroxide ion ➞ oxygen + water solution • The product of
+ electrons electrolysis at the
cathode is hydrogen
Cell II gas (colourless gas)
• The chloride ion is selected to be
discharged because it has higher The electrolyte consists of
concentration.
• The product of electrolysis at the Anions Cations
anode is chlorine gas (colourless A chloride ion sodium ion
gas)
• Chloride ion ➞ chlorine + electrons hydroxide ion hydrogen ion
Figure 6.5 Electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution Form 5
(iii) Type of electrodes used
Example 4
Electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution using carbon or copper electrodes:
Anode Electrolysis of copper(II) Cathode
sulphate solution using
Cell I different electrodes In both cell I and cell II
• Carbon electrodes (inert electrodes) Cell I: Carbon electrodes • Copper(II) ions
• The hydroxide ion is selected to be Cell II: Copper electrodes and hydrogen ions
discharged because its position move toward the
in the electrochemical series is cathode.
lower. • The copper(II) ion
• Oxygen gas is released as the is selected to be
product. discharged because
• Hydroxide ion ➞ oxygen + water Carbon/ Carbon/ its position in the
+ electrons copper copper electrochemical
Cell II electrode electrode series is lower.
• Copper electrodes (reactive Copper(II) • The product of
electrodes) sulphate electrolysis at the
• The copper electrode dissolves solution cathode is copper
to form copper(II) ions metal (brown solid).
• Copper atom ➞ copper(II) ion + The electrolyte consists of • A brown solid is
electrons Anions Cations deposited on the
• Copper(II) ions are formed as cathode (cathode
the product sulphate Ion copper ion thickens)
• The copper anode becomes hydroxide ion hydrogen ion • Copper(II) ion +
thinner electrons ➞ copper
Figure 6.6 Electrolysis of copper(II) sulphate solution
287
F5 Chapter 6.indd 287 3/21/22 3:59 PM