Page 119 - Essentials of Nursing Leadership and Management, 5th Edition
P. 119
CikguOnline
2208_Ch08_103-114.qxd 11/6/09 5:58 PM Page 106
106 unit 2 | Working Within the Organization CikguOnline
committee recognized that this objection was based needs (those lower on the hierarchy) must be at
on technical concerns and requested a study of least partially met before a person is motivated to
the evidence before instituting the change. “It’s seek fulfillment of the higher-order needs.
important to investigate the evidence supporting a Change may make it more difficult for a person
proposed change thoroughly before recommending to meet any or all of his or her needs. It may
it,” she said. threaten the powerful safety and security needs that
Maslow discussed (Hunter, 2004). For example, if a
A change may provide resistance for practical rea-
massive downsizing occurs and a person’s job is
sons. For example, if the bar codes on patients’arm-
eliminated, fulfillment of all of these levels of needs
bands are difficult to scan, nurses may develop a
may be threatened, from having enough money to
way to work around this safety feature by taping a
pay for food and shelter to opportunities to fulfill
duplicate armband to the bed or to a clipboard
one’s career potential.
(Englebright & Franklin, 2005), defeating the
In other cases, the threat is subtler and may be
purpose of instituting electronically monitored
harder to anticipate.For example,an institution-wide
medication administration.
reevaluation of the effectiveness of the advanced
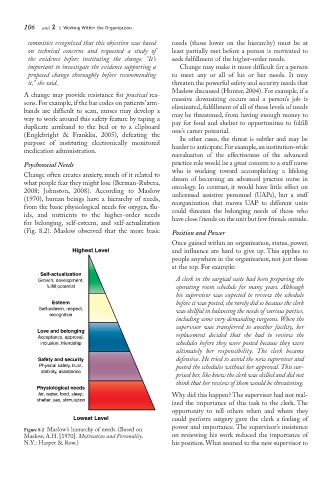
Psychosocial Needs practice role would be a great concern to a staff nurse
who is working toward accomplishing a lifelong
Change often creates anxiety, much of it related to
dream of becoming an advanced practice nurse in
what people fear they might lose (Berman-Rubera,
oncology. In contrast, it would have little effect on
2008; Johnston, 2008). According to Maslow
unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs), but a staff
(1970), human beings have a hierarchy of needs,
reorganization that moves UAP to different units
from the basic physiological needs for oxygen, flu-
could threaten the belonging needs of those who
ids, and nutrients to the higher-order needs
have close friends on the unit but few friends outside.
for belonging, self-esteem, and self-actualization
(Fig. 8.2). Maslow observed that the more basic Position and Power
Once gained within an organization, status, power,
Highest Level and influence are hard to give up. This applies to
people anywhere in the organization, not just those
at the top. For example:
Self-actualization
Growth, development, A clerk in the surgical suite had been preparing the
fulfill potential operating room schedule for many years. Although
his supervisor was expected to review the schedule
Esteem before it was posted, she rarely did so because the clerk
Self-esteem, respect, was skillful in balancing the needs of various parties,
recognition
including some very demanding surgeons. When the
supervisor was transferred to another facility, her
Love and belonging
Acceptance, approval, replacement decided that she had to review the
inclusion, friendship schedules before they were posted because they were
ultimately her responsibility. The clerk became
Safety and security defensive. He tried to avoid the new supervisor and
Physical safety, trust, posted the schedules without her approval. This sur-
stability, assistance
prised her. She knew the clerk was skilled and did not
think that her review of them would be threatening.
Physiological needs
Air, water, food, sleep, Why did this happen? The supervisor had not real-
shelter, sex, stimulation
ized the importance of this task to the clerk. The
opportunity to tell others when and where they
Lowest Level could perform surgery gave the clerk a feeling of
power and importance. The supervisor’s insistence
Figure 8.2 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. (Based on
Maslow, A.H. [1970]. Motivation and Personality. on reviewing his work reduced the importance of
N.Y.: Harper & Row.) his position.What seemed to the new supervisor to