Page 138 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 138
124 PHYSICS
2
external force F does work + kx / 2 . If the block and vice versa, however, the total mechanical
c energy remains constant. This is graphically
is moved from an initial displacement x to a
i depicted in Fig. 6.8.
final displacement x , the work done by the
f
spring force W is
s
x f k x 2 k x 2
d
W = − ∫ k x x = 2 i − 2 f (6.17)
s
x i
Thus the work done by the spring force depends
only on the end points. Specifically, if the block
is pulled from x and allowed to return to x ;
i i
x i k x 2 k x 2
W = − ∫ k x x =d i − i
s
2 2
x i
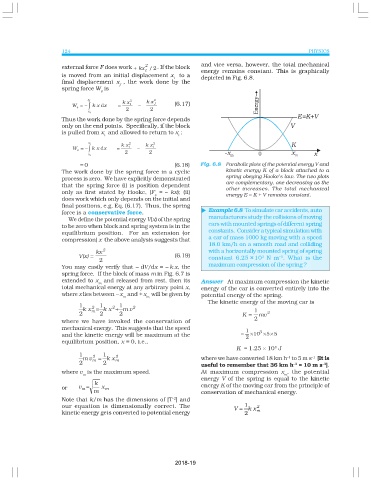
= 0 (6.18) Fig. 6.8 Parabolic plots of the potential energy V and
The work done by the spring force in a cyclic kinetic energy K of a block attached to a
process is zero. We have explicitly demonstrated spring obeying Hooke’s law. The two plots
that the spring force (i) is position dependent are complementary, one decreasing as the
other increases. The total mechanical
only as first stated by Hooke, (F = − kx); (ii)
s energy E = K + V remains constant.
does work which only depends on the initial and
final positions, e.g. Eq. (6.17). Thus, the spring
force is a conservative force. t Example 6.8 To simulate car accidents, auto
We define the potential energy V(x) of the spring manufacturers study the collisions of moving
to be zero when block and spring system is in the cars with mounted springs of different spring
equilibrium position. For an extension (or constants. Consider a typical simulation with
compression) x the above analysis suggests that a car of mass 1000 kg moving with a speed
18.0 km/h on a smooth road and colliding
kx 2 with a horizontally mounted spring of spring
V(x) = (6.19) constant 6.25 × 10 3 N m . What is the
–1
2
You may easily verify that − dV/dx = − k x, the maximum compression of the spring ?
spring force. If the block of mass m in Fig. 6.7 is
extended to x and released from rest, then its Answer At maximum compression the kinetic
m
total mechanical energy at any arbitrary point x, energy of the car is converted entirely into the
where x lies between – x and + x will be given by potential energy of the spring.
m m,
The kinetic energy of the moving car is
1 2 1 2 1 2
x k m = x k + m v 1
2 2 2 K = mv 2
where we have invoked the conservation of 2
mechanical energy. This suggests that the speed 1 3
and the kinetic energy will be maximum at the = 2 × 10 × 5 × 5
equilibrium position, x = 0, i.e.,
K = 1.25 × 10 J
4
1 2 1 2
–1
–1
m v m = x k m where we have converted 18 km h to 5 m s [It is
2 2 useful to remember that 36 km h = 10 m s ].
–1
–1
where v is the maximum speed. At maximum compression x , the potential
m m
energy V of the spring is equal to the kinetic
k energy K of the moving car from the principle of
or v = x m
m
m conservation of mechanical energy.
Note that k/m has the dimensions of [T ] and
-2
our equation is dimensionally correct. The V = 1 x k 2
kinetic energy gets converted to potential energy 2 m
2018-19