Page 7 - Chemistry Terminologies SK015 & DK014_Chemistry Unit, KMNS
P. 7
Chemistry Terminologies
Chapter 3 : Periodic Table
Chemistry Unit KMNS
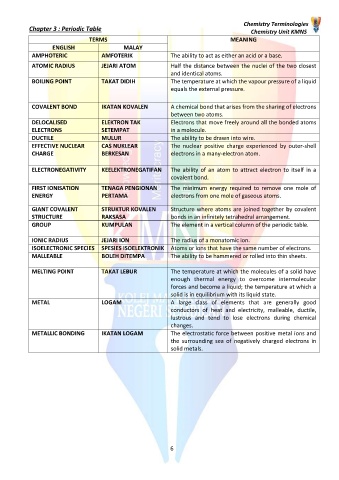
TERMS MEANING
ENGLISH MALAY
AMPHOTERIC AMFOTERIK The ability to act as either an acid or a base.
ATOMIC RADIUS JEJARI ATOM Half the distance between the nuclei of the two closest
and identical atoms.
BOILING POINT TAKAT DIDIH The temperature at which the vapour pressure of a liquid
equals the external pressure.
COVALENT BOND IKATAN KOVALEN A chemical bond that arises from the sharing of electrons
between two atoms.
DELOCALISED ELEKTRON TAK Electrons that move freely around all the bonded atoms
ELECTRONS SETEMPAT in a molecule.
DUCTILE MULUR The ability to be drawn into wire.
EFFECTIVE NUCLEAR CAS NUKLEAR The nuclear positive charge experienced by outer-shell
CHARGE BERKESAN electrons in a many-electron atom.
ELECTRONEGATIVITY KEELEKTRONEGATIFAN The ability of an atom to attract electron to itself in a
covalent bond.
FIRST IONISATION TENAGA PENGIONAN The minimum energy required to remove one mole of
ENERGY PERTAMA electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms.
GIANT COVALENT STRUKTUR KOVALEN Structure where atoms are joined together by covalent
STRUCTURE RAKSASA bonds in an infinitely tetrahedral arrangement.
GROUP KUMPULAN The element in a vertical column of the periodic table.
IONIC RADIUS JEJARI ION The radius of a monatomic ion.
ISOELECTRONIC SPECIES SPESIES ISOELEKTRONIK Atoms or ions that have the same number of electrons.
MALLEABLE BOLEH DITEMPA The ability to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets.
MELTING POINT TAKAT LEBUR The temperature at which the molecules of a solid have
enough thermal energy to overcome intermolecular
forces and become a liquid; the temperature at which a
solid is in equilibrium with its liquid state.
METAL LOGAM A large class of elements that are generally good
conductors of heat and electricity, malleable, ductile,
lustrous and tend to lose electrons during chemical
changes.
METALLIC BONDING IKATAN LOGAM The electrostatic force between positive metal ions and
the surrounding sea of negatively charged electrons in
solid metals.
6