Page 12 - Chemistry Terminologies SK015 & DK014_Chemistry Unit, KMNS
P. 12
Chemistry Terminologies
Chapter 5 : States of Matter Chemistry Unit KMNS
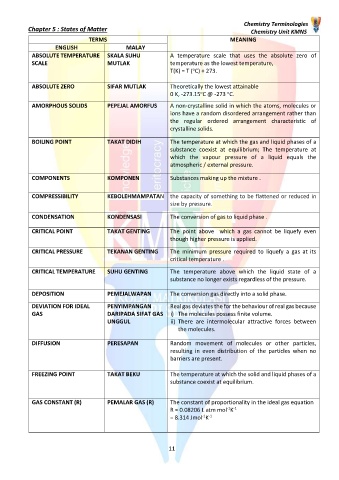
TERMS MEANING
ENGLISH MALAY
ABSOLUTE TEMPERATURE SKALA SUHU A temperature scale that uses the absolute zero of
SCALE MUTLAK temperature as the lowest temperature,
o
T(K) = T ( C) + 273.
ABSOLUTE ZERO SIFAR MUTLAK Theoretically the lowest attainable
o
o
0 K, -273.15 C @ -273 C.
AMORPHOUS SOLIDS PEPEJAL AMORFUS A non-crystalline solid in which the atoms, molecules or
ions have a random disordered arrangement rather than
the regular ordered arrangement characteristic of
crystalline solids.
BOILING POINT TAKAT DIDIH The temperature at which the gas and liquid phases of a
substance coexist at equilibrium; The temperature at
which the vapour pressure of a liquid equals the
atmospheric / external pressure.
COMPONENTS KOMPONEN Substances making up the mixture .
COMPRESSIBILITY KEBOLEHMAMPATAN the capacity of something to be flattened or reduced in
size by pressure.
CONDENSATION KONDENSASI The conversion of gas to liquid phase .
CRITICAL POINT TAKAT GENTING The point above which a gas cannot be liquefy even
though higher pressure is applied.
CRITICAL PRESSURE TEKANAN GENTING The minimum pressure required to liquefy a gas at its
critical temperature .
CRITICAL TEMPERATURE SUHU GENTING The temperature above which the liquid state of a
substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure.
DEPOSITION PEMEJALWAPAN The conversion gas directly into a solid phase.
DEVIATION FOR IDEAL PENYIMPANGAN Real gas deviates the for the behaviour of real gas because
GAS DARIPADA SIFAT GAS i) The molecules possess finite volume.
UNGGUL ii) There are intermolecular attractive forces between
the molecules.
DIFFUSION PERESAPAN Random movement of molecules or other particles,
resulting in even distribution of the particles when no
barriers are present.
FREEZING POINT TAKAT BEKU The temperature at which the solid and liquid phases of a
substance coexist at equilibrium.
GAS CONSTANT (R) PEMALAR GAS (R) The constant of proportionality in the ideal gas equation
-1 -1
R = 0.08206 L atm mol K
-1 -1
= 8.314 Jmol K
11