Page 54 - analysis-and-interpretation-of-astronomical-sp
P. 54
Analysis and Interpretation of Astronomical Spectra 54
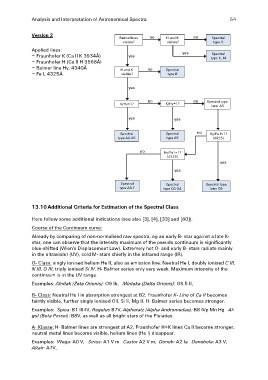
Version 2 Balmerlines no H and K no Spectral
visible? visible? type O
Applied lines: Spectral
– Fraunhofer K (Ca II K 3934Å) yes yes type K, M
– Fraunhofer H (Ca II H 3968Å)
– Balmer line Hγ, 4340Å H and K no Spectral
– Fe I, 4325Å visible? type B
yes
K/Hγ<1? no K/Hγ=1? no Spectral type
later A5
yes yes
Spectral Spectral no Hγ/Fe I<1?
type A0-A5 type A5
(4325)
no Hγ/Fe I=1? yes
(4325)
yes
Spectral Spectral Spectral type
type A6-F type G0-G4 later G5
13.10 Additional Criteria for Estimation of the Spectral Class
Here follow some additional indications (see also [3], [4], [33] and [80]).
Course of the Continuum curve:
Already by comparing of non-normalised raw spectra, eg an early B- star against a late K-
star, one can observe that the intensity maximum of the pseudo continuum is significantly
blue-shifted (Wien's Displacement Law). Extremely hot O- and early B- stars radiate mainly
in the ultraviolet (UV), cold M- stars chiefly in the infrared range (IR).
O- Class: singly ionised helium He II, also as emission line. Neutral He I, doubly ionised C III,
N III, O III, triply ionised Si IV. H- Balmer series only very weak. Maximum intensity of the
continuum is in the UV range.
Examples: Alnitak (Zeta Orionis): O9 Ib, Mintaka (Delta Orionis): O9.5 II,
B- Class: Neutral He I in absorption strongest at B2, Fraunhofer K- Line of Ca II becomes
faintly visible, further singly ionised OII, Si II, Mg II. H- Balmer series becomes stronger.
Examples: Spica: B1 III-IV, Regulus B7V, Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae): B8 IVp Mn Hg Al-
gol (Beta Persei): B8V, as well as all bright stars of the Pleiades.
A- Klasse: H- Balmer lines are strongest at A2, Fraunhofer H+K lines Ca II become stronger,
neutral metal lines become visible, helium lines (He I) disappear.
Examples: Wega: A0 V, Sirius: A1 V m Castor A2 V m, Deneb: A2 Ia Denebola: A3 V,
Altair: A7V,