Page 43 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 43
THE FORMATION OF THE EARTH 41
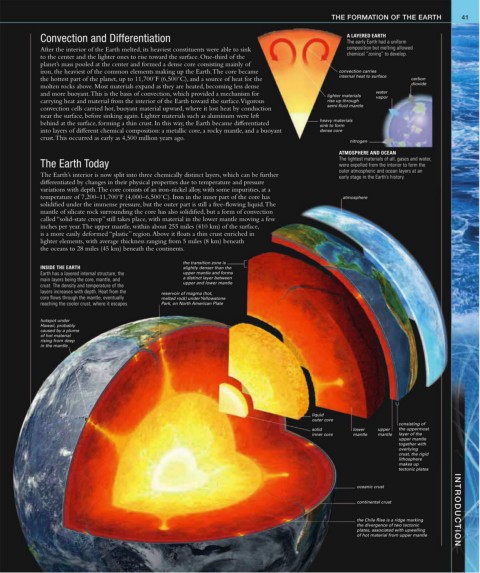
Convection and Differentiation A LAYERED EARTH
The early Earth had a uniform
After the interior of the Earth melted, its heaviest constituents were able to sink composition but melting allowed
to the center and the lighter ones to rise toward the surface. One-third of the chemical “zoning” to develop.
planet’s mass pooled at the center and formed a dense core consisting mainly of
iron, the heaviest of the common elements making up the Earth. The core became convection carries
internal heat to surface
the hottest part of the planet, up to 11,700˚F (6,500˚C), and a source of heat for the carbon
molten rocks above. Most materials expand as they are heated, becoming less dense dioxide
and more buoyant. This is the basis of convection, which provided a mechanism for lighter materials water
vapor
carrying heat and material from the interior of the Earth toward the surface. Vigorous rise up through
semi-fluid mantle
convection cells carried hot, buoyant material upward, where it lost heat by conduction
near the surface, before sinking again. Lighter materials such as aluminum were left
heavy materials
behind at the surface, forming a thin crust. In this way, the Earth became differentiated
sink to form
into layers of different chemical composition: a metallic core, a rocky mantle, and a buoyant dense core
crust. This occurred as early as 4,500 million years ago.
nitrogen
ATMOSPHERE AND OCEAN
The lightest materials of all, gases and water,
The Earth Today were expelled from the interior to form the
outer atmospheric and ocean layers at an
The Earth’s interior is now split into three chemically distinct layers, which can be further early stage in the Earth’s history.
differentiated by changes in their physical properties due to temperature and pressure
variations with depth. The core consists of an iron-nickel alloy, with some impurities, at a
temperature of 7,200–11,700˚F (4,000–6,500˚C). Iron in the inner part of the core has atmosphere
solidified under the immense pressure, but the outer part is still a free-flowing liquid. The
mantle of silicate rock surrounding the core has also solidified, but a form of convection
called “solid-state creep” still takes place, with material in the lower mantle moving a few
inches per year. The upper mantle, within about 255 miles (410 km) of the surface,
is a more easily deformed “plastic” region. Above it floats a thin crust enriched in
lighter elements, with average thickness ranging from 5 miles (8 km) beneath
the oceans to 28 miles (45 km) beneath the continents.
the transition zone is
INSIDE THE EARTH slightly denser than the
Earth has a layered internal structure, the upper mantle and forms
main layers being the core, mantle, and a distinct layer between
crust. The density and temperature of the upper and lower mantle
layers increases with depth. Heat from the reservoir of magma (hot,
core flows through the mantle, eventually melted rock) under Yellowstone
reaching the cooler crust, where it escapes. Park, on North American Plate
hotspot under
Hawaii, probably
caused by a plume
of hot material
rising from deep
in the mantle
liquid
outer core
consisting of
solid lower upper the uppermost
inner core mantle mantle layer of the
upper mantle
together with
overlying
crust, the rigid
lithosphere
makes up
tectonic plates
oceanic crust
continental crust INTRODUCTION
the Chile Rise is a ridge marking
the divergence of two tectonic
plates, associated with upwelling
of hot material from upper mantle