Page 45 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 45
THE ORIGIN OF OCEANS AND CONTINENTS 43
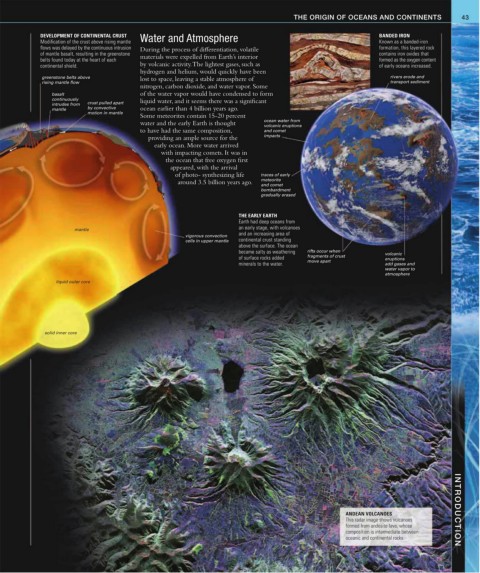
DEVELOPMENT OF CONTINENTAL CRUST Water and Atmosphere BANDED IRON
Modification of the crust above rising mantle Known as a banded-iron
flows was delayed by the continuous intrusion During the process of differentiation, volatile formation, this layered rock
of mantle basalt, resulting in the greenstone contains iron oxides that
belts found today at the heart of each materials were expelled from Earth’s interior formed as the oxygen content
continental shield. by volcanic activity. The lightest gases, such as of early oceans increased.
hydrogen and helium, would quickly have been
greenstone belts above lost to space, leaving a stable atmosphere of rivers erode and
rising mantle flow transport sediment
nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Some
basalt of the water vapor would have condensed to form
continuously liquid water, and it seems there was a significant
intrudes from crust pulled apart
mantle by convective ocean earlier than 4 billion years ago.
motion in mantle
Some meteorites contain 15-20 percent
water and the early Earth is thought ocean water from
volcanic eruptions
to have had the same composition, and comet
providing an ample source for the impacts
early ocean. More water arrived
with impacting comets. It was in
the ocean that free oxygen first
appeared, with the arrival
of photo- synthesizing life traces of early
around 3.5 billion years ago. meteorite
and comet
bombardment
gradually erased
THE EARLY EARTH
Earth had deep oceans from
an early stage, with volcanoes
mantle
and an increasing area of
vigorous convection
cells in upper mantle continental crust standing
above the surface. The ocean
became salty as weathering rifts occur when volcanic
of surface rocks added fragments of crust eruptions
move apart
minerals to the water. add gases and
water vapor to
atmosphere
liquid outer core
solid inner core
ANDEAN VOLCANOES INTRODUCTION
This radar image shows volcanoes
formed from andesite lava, whose
composition is intermediate between
oceanic and continental rocks.