Page 12 - (DK) The Dog Encyclopedia
P. 12
INTRODUCTION TO DOGS | SKELETON AND MUSCLE
Skeleton and muscle
All mammals have a skeleton that is stabilized and given mobility by ligaments, tendons, and
muscles. In dogs, this system evolved to serve their ancestral needs as fast-running carnivores.
However, once domesticated, humans created different dogs for different tasks and in doing so
altered their skeletons, too. Although some changes, such as dwarfism, result naturally from
mutations, deliberate selection has created most of the variety seen in modern breeds today.
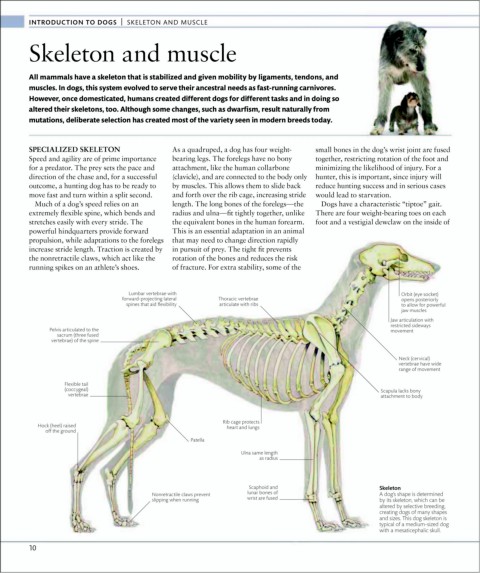
SPECIALIZED SKELETON As a quadruped, a dog has four weight- small bones in the dog’s wrist joint are fused
Speed and agility are of prime importance bearing legs. The forelegs have no bony together, restricting rotation of the foot and
for a predator. The prey sets the pace and attachment, like the human collarbone minimizing the likelihood of injury. For a
direction of the chase and, for a successful (clavicle), and are connected to the body only hunter, this is important, since injury will
outcome, a hunting dog has to be ready to by muscles. This allows them to slide back reduce hunting success and in serious cases
move fast and turn within a split second. and forth over the rib cage, increasing stride would lead to starvation.
Much of a dog’s speed relies on an length. The long bones of the forelegs—the Dogs have a characteristic “tiptoe” gait.
extremely flexible spine, which bends and radius and ulna—fit tightly together, unlike There are four weight-bearing toes on each
stretches easily with every stride. The the equivalent bones in the human forearm. foot and a vestigial dewclaw on the inside of
powerful hindquarters provide forward This is an essential adaptation in an animal
propulsion, while adaptations to the forelegs that may need to change direction rapidly
increase stride length. Traction is created by in pursuit of prey. The tight fit prevents
the nonretractile claws, which act like the rotation of the bones and reduces the risk
running spikes on an athlete’s shoes. of fracture. For extra stability, some of the
Lumbar vertebrae with Orbit (eye socket)
forward-projecting lateral Thoracic vertebrae opens posteriorly
spines that aid flexibility articulate with ribs to allow for powerful
jaw muscles
Jaw articulation with
restricted sideways
Pelvis articulated to the movement
sacrum (three fused
vertebrae) of the spine
Neck (cervical)
vertebrae have wide
range of movement
Flexible tail
(coccygeal) Scapula lacks bony
vertebrae attachment to body
Rib cage protects
Hock (heel) raised heart and lungs
off the ground
Patella
Ulna same length
as radius
Scaphoid and Skeleton
lunar bones of
Nonretractile claws prevent A dog’s shape is determined
slipping when running wrist are fused by its skeleton, which can be
altered by selective breeding,
creating dogs of many shapes
and sizes. This dog skeleton is
typical of a medium-sized dog
with a mesaticephalic skull.
10