Page 15 - (DK) The Dog Encyclopedia
P. 15
SENSES
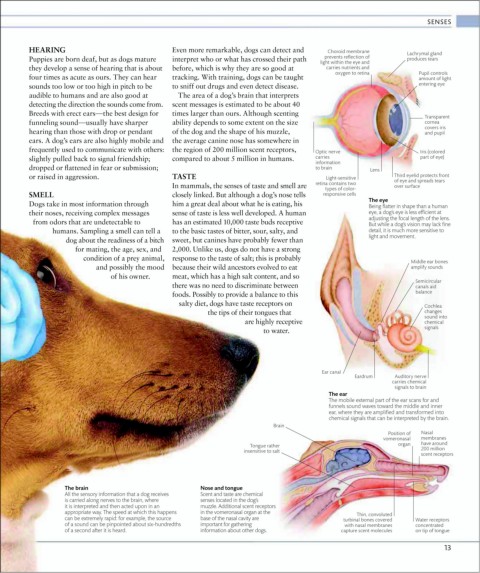
HEARING Even more remarkable, dogs can detect and Choroid membrane Lachrymal gland
Puppies are born deaf, but as dogs mature interpret who or what has crossed their path prevents reflection of produces tears
light within the eye and
they develop a sense of hearing that is about before, which is why they are so good at carries nutrients and
oxygen to retina Pupil controls
four times as acute as ours. They can hear tracking. With training, dogs can be taught amount of light
sounds too low or too high in pitch to be to sniff out drugs and even detect disease. entering eye
audible to humans and are also good at The area of a dog’s brain that interprets
detecting the direction the sounds come from. scent messages is estimated to be about 40
Breeds with erect ears—the best design for times larger than ours. Although scenting
Transparent
funneling sound—usually have sharper ability depends to some extent on the size cornea
covers iris
hearing than those with drop or pendant of the dog and the shape of his muzzle, and pupil
ears. A dog’s ears are also highly mobile and the average canine nose has somewhere in
frequently used to communicate with others: the region of 200 million scent receptors, Optic nerve Iris (colored
slightly pulled back to signal friendship; compared to about 5 million in humans. carries part of eye)
information
dropped or flattened in fear or submission; to brain Lens
or raised in aggression. TASTE Light-sensitive Third eyelid protects front
of eye and spreads tears
In mammals, the senses of taste and smell are retina contains two over surface
types of color-
SMELL closely linked. But although a dog’s nose tells responsive cells
The eye
Dogs take in most information through him a great deal about what he is eating, his Being flatter in shape than a human
their noses, receiving complex messages sense of taste is less well developed. A human eye, a dog’s eye is less efficient at
adjusting the focal length of the lens.
from odors that are undetectable to has an estimated 10,000 taste buds receptive But while a dog’s vision may lack fine
humans. Sampling a smell can tell a to the basic tastes of bitter, sour, salty, and detail, it is much more sensitive to
light and movement.
dog about the readiness of a bitch sweet, but canines have probably fewer than
for mating, the age, sex, and 2,000. Unlike us, dogs do not have a strong
condition of a prey animal, response to the taste of salt; this is probably
Middle ear bones
and possibly the mood because their wild ancestors evolved to eat amplify sounds
of his owner. meat, which has a high salt content, and so
Semicircular
there was no need to discriminate between canals aid
foods. Possibly to provide a balance to this balance
salty diet, dogs have taste receptors on
Cochlea
the tips of their tongues that changes
sound into
are highly receptive chemical
signals
to water.
Ear canal
Eardrum Auditory nerve
carries chemical
signals to brain
The ear
The mobile external part of the ear scans for and
funnels sound waves toward the middle and inner
ear, where they are amplified and transformed into
chemical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
Brain
Position of Nasal
vomeronasal membranes
Tongue rather organ have around
insensitive to salt 200 million
scent receptors
The brain Nose and tongue
All the sensory information that a dog receives Scent and taste are chemical
is carried along nerves to the brain, where senses located in the dog’s
it is interpreted and then acted upon in an muzzle. Additional scent receptors
appropriate way. The speed at which this happens in the vomeronasal organ at the Thin, convoluted
can be extremely rapid: for example, the source base of the nasal cavity are turbinal bones covered Water receptors
of a sound can be pinpointed about six-hundredths important for gathering with nasal membranes concentrated
of a second after it is heard. information about other dogs. capture scent molecules on tip of tongue
13