Page 13 - (DK) The Dog Encyclopedia
P. 13
SKELETON AND MUSCLE
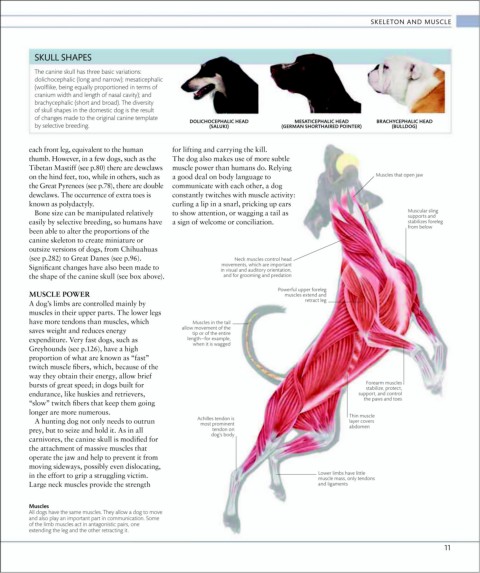
SKULL SHAPES
The canine skull has three basic variations:
dolichocephalic (long and narrow); mesaticephalic
(wolflike, being equally proportioned in terms of
cranium width and length of nasal cavity); and
brachycephalic (short and broad). The diversity
of skull shapes in the domestic dog is the result
of changes made to the original canine template
DOLICHOCEPHALIC HEAD MESATICEPHALIC HEAD BRACHYCEPHALIC HEAD
by selective breeding. (SALUKI) (GERMAN SHORTHAIRED POINTER) (BULLDOG)
each front leg, equivalent to the human for lifting and carrying the kill.
thumb. However, in a few dogs, such as the The dog also makes use of more subtle
Tibetan Mastiff (see p.80) there are dewclaws muscle power than humans do. Relying
on the hind feet, too, while in others, such as a good deal on body language to Muscles that open jaw
the Great Pyrenees (see p.78), there are double communicate with each other, a dog
dewclaws. The occurrence of extra toes is constantly twitches with muscle activity:
known as polydactyly. curling a lip in a snarl, pricking up ears
Bone size can be manipulated relatively to show attention, or wagging a tail as Muscular sling
supports and
easily by selective breeding, so humans have a sign of welcome or conciliation. stabilizes foreleg
from below
been able to alter the proportions of the
canine skeleton to create miniature or
outsize versions of dogs, from Chihuahuas
(see p.282) to Great Danes (see p.96). Neck muscles control head
movements, which are important
Significant changes have also been made to
in visual and auditory orientation,
the shape of the canine skull (see box above). and for grooming and predation
Powerful upper foreleg
MUSCLE POWER muscles extend and
retract leg
A dog’s limbs are controlled mainly by
muscles in their upper parts. The lower legs
have more tendons than muscles, which Muscles in the tail
saves weight and reduces energy allow movement of the
tip or of the entire
expenditure. Very fast dogs, such as length—for example,
when it is wagged
Greyhounds (see p.126), have a high
proportion of what are known as “fast”
twitch muscle fibers, which, because of the
way they obtain their energy, allow brief
bursts of great speed; in dogs built for Forearm muscles
stabilize, protect,
endurance, like huskies and retrievers, support, and control
the paws and toes
“slow” twitch fibers that keep them going
longer are more numerous.
Thin muscle
A hunting dog not only needs to outrun Achilles tendon is layer covers
most prominent abdomen
prey, but to seize and hold it. As in all tendon on
dog’s body
carnivores, the canine skull is modified for
the attachment of massive muscles that
operate the jaw and help to prevent it from
moving sideways, possibly even dislocating,
in the effort to grip a struggling victim. Lower limbs have little
muscle mass, only tendons
Large neck muscles provide the strength and ligaments
Muscles
All dogs have the same muscles. They allow a dog to move
and also play an important part in communication. Some
of the limb muscles act in antagonistic pairs, one
extending the leg and the other retracting it.
11