Page 19 - (DK) The Dog Encyclopedia
P. 19
URINARY, REPRODUCTIVE, AND HORMONAL SYSTEMS
REPRODUCTION Anything from one to fourteen or more
Dogs usually reach sexual maturity puppies may be born, but a litter of six HORMONES IN
somewhere between 6 and 12 months of age. to eight is the average. PREGNANCY
In wild canines such as the wolf, females
During pregnancy, rising levels of hormones
normally have one period of estrus a year HORMONES
such as estrogen help to prepare a bitch
(known as “coming into season,” or being Produced by specialized glands and tissues
for giving birth and also, by stimulating
“in heat”), during which they ovulate and and released into the bloodstream, hormones development of the milk glands, for feeding
are ready to breed. With a few exceptions, are chemicals that affect specific cells. her puppies. In a lactating (nursing) bitch, milk
the Basenji being one, domestic dogs usually Hormonal activity controls many body production is maintained by an increase in the
have two seasons a year. The onset of estrus functions, including growth, metabolism, hormone prolactin, which also influences
maternal behavior, arousing strong protective
is marked by a small discharge of blood, sexual development, and reproduction.
instincts and ensuring that the mother will not
which lasts for around nine days, after Neutering dogs removes the production desert her puppies while they are still totally
which the bitch will be willing to mate. sites of the sex hormones—testosterone in dependent on her for survival.
Male dogs have a bone within the penis males, and estrogen in females—and
called the baculum. During mating, the prevents unwanted pregnancies. As a result
area around the bone enlarges, locking of the loss of testosterone, male dogs lose the
the penis inside the female and creating urge to wander in search of females and are
what is known as the “tie,” which can last less likely to show aggression. Neutering also
for some minutes. If mating leads to affects coat shedding in bitches, which usually
fertilization of the female ova (eggs), the have their heaviest coat loss twice a year,
pregnancy that follows will last between triggered by the hormone that brings them
60 to 68 days. The size of the litter into season. Spayed (neutered) females tend
depends on the type of dog, with larger to shed all year round. Neutering may also
breeds tending to have larger litters. increase the probability of obesity in later life.
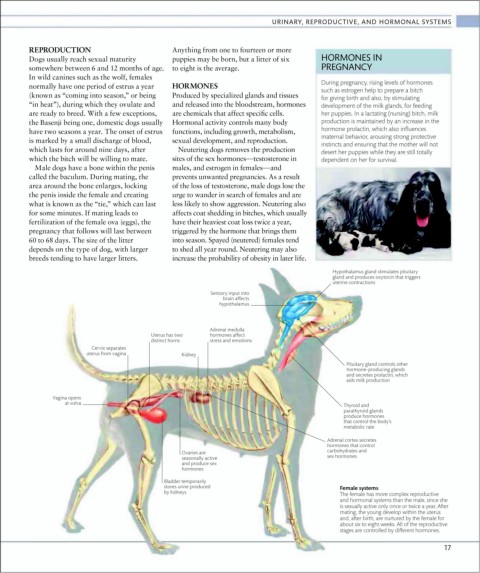
Hypothalamus gland stimulates pituitary
gland and produces oxytocin that triggers
uterine contractions
Sensory input into
brain affects
hypothalamus
Adrenal medulla
Uterus has two hormones affect
distinct horns stress and emotions
Cervix separates
uterus from vagina Kidney
Pituitary gland controls other
hormone-producing glands
and secretes prolactin, which
aids milk production
Vagina opens
at vulva
Thyroid and
parathyroid glands
produce hormones
that control the body’s
metabolic rate
Adrenal cortex secretes
hormones that control
carbohydrates and
Ovaries are
seasonally active sex hormones
and produce sex
hormones
Bladder temporarily
stores urine produced Female systems
by kidneys The female has more complex reproductive
and hormonal systems than the male, since she
is sexually active only once or twice a year. After
mating, the young develop within the uterus
and, after birth, are nurtured by the female for
about six to eight weeks. All of the reproductive
stages are controlled by different hormones.
17