Page 103 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 103
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS SECTION II 59
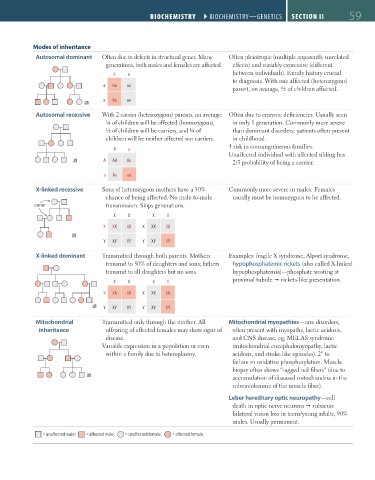
Modes of inheritance
Autosomal dominant Often due to defects in structural genes. Many Often pleiotropic (multiple apparently unrelated
generations, both males and females are affected. effects) and variably expressive (different
A a between individuals). Family history crucial
to diagnosis. With one affected (heterozygous)
a Aa aa
parent, on average, 1/2 of children affected.
a Aa aa
Autosomal recessive With 2 carrier (heterozygous) parents, on average: Often due to enzyme deficiencies. Usually seen
¼ of children will be affected (homozygous), in only 1 generation. Commonly more severe
1/2 of children will be carriers, and ¼ of than dominant disorders; patients often present
children will be neither affected nor carriers. in childhood.
risk in consanguineous families.
A a
Unaffected individual with affected sibling has
A AA Aa 2/3 probability of being a carrier.
a Aa aa
X-linked recessive Sons of heterozygous mothers have a 50% Commonly more severe in males. Females
chance of being affected. No male-to-male usually must be homozygous to be affected.
carrier transmission. Skips generations.
X X X X
X XX XX X XX XX
Y XY XY Y XY XY
X-linked dominant Transmitted through both parents. Mothers Examples: fragile X syndrome, Alport syndrome,
transmit to 50% of daughters and sons; fathers hypophosphatemic rickets (also called X-linked
transmit to all daughters but no sons. hypophosphatemia)—phosphate wasting at
proximal tubule rickets-like presentation.
X X X X
X XX XX X XX XX
Y XY XY Y XY XY
Mitochondrial Transmitted only through the mother. All Mitochondrial myopathies—rare disorders;
inheritance offspring of affected females may show signs of often present with myopathy, lactic acidosis,
disease. and CNS disease, eg, MELAS syndrome
Variable expression in a population or even (mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic
within a family due to heteroplasmy. acidosis, and stroke-like episodes). 2° to
failure in oxidative phosphorylation. Muscle
biopsy often shows “ragged red fibers” (due to
accumulation of diseased mitochondria in the
subsarcolemma of the muscle fiber).
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy—cell
death in optic nerve neurons subacute
bilateral vision loss in teens/young adults, 90%
males. Usually permanent.
= una ected male; = a ected male; = una ected female; = a ected female.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 59 11/7/19 3:16 PM