Page 98 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 98
54 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES
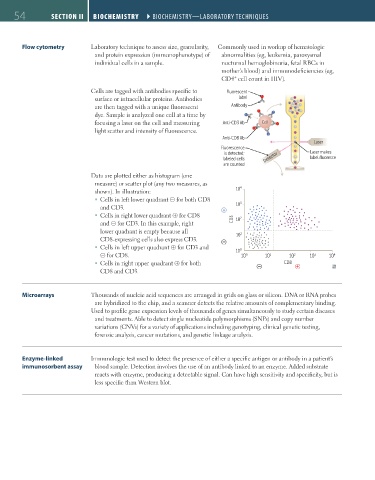
Flow cytometry Laboratory technique to assess size, granularity, Commonly used in workup of hematologic
and protein expression (immunophenotype) of abnormalities (eg, leukemia, paroxysmal
individual cells in a sample. nocturnal hemoglobinuria, fetal RBCs in
mother’s blood) and immunodeficiencies (eg,
+
CD4 cell count in HIV).
Cells are tagged with antibodies specific to Fluorescent
surface or intracellular proteins. Antibodies label
are then tagged with a unique fluorescent Antibody
dye. Sample is analyzed one cell at a time by
focusing a laser on the cell and measuring Anti-CD3 Ab Cell
light scatter and intensity of fluorescence.
Anti-CD8 Ab
Laser
Fluorescence
is detected; Laser makes
labeled cells Detector label fluoresce
are counted
Data are plotted either as histogram (one
measure) or scatter plot (any two measures, as
shown). In illustration: 10 4
Cells in left lower quadrant ⊝ for both CD8
and CD3. 10 3
Cells in right lower quadrant ⊕ for CD8 2
and ⊝ for CD3. In this example, right CD3 10
lower quadrant is empty because all 1
CD8-expressing cells also express CD3. 10
Cells in left upper quadrant ⊕ for CD3 and 0
⊝ for CD8. 10 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4
Cells in right upper quadrant ⊕ for both CD8
CD8 and CD3.
Microarrays Thousands of nucleic acid sequences are arranged in grids on glass or silicon. DNA or RNA probes
are hybridized to the chip, and a scanner detects the relative amounts of complementary binding.
Used to profile gene expression levels of thousands of genes simultaneously to study certain diseases
and treatments. Able to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number
variations (CNVs) for a variety of applications including genotyping, clinical genetic testing,
forensic analysis, cancer mutations, and genetic linkage analysis.
Enzyme-linked Immunologic test used to detect the presence of either a specific antigen or antibody in a patient’s
immunosorbent assay blood sample. Detection involves the use of an antibody linked to an enzyme. Added substrate
reacts with enzyme, producing a detectable signal. Can have high sensitivity and specificity, but is
less specific than Western blot.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 54 11/7/19 3:16 PM