Page 101 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 101
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS SECTION II 57
Genetic terms (continued)
TERM DEFINITION EXAMPlE
Dominant negative Exerts a dominant effect. A heterozygote A single mutated p53 tumor suppressor gene
mutation produces a nonfunctional altered protein that results in a protein that is able to bind DNA and
also prevents the normal gene product from block the nonmutated p53 from binding to the
functioning. promoter.
Linkage Tendency for certain alleles at 2 linked
disequilibrium loci to occur together more or less often
than expected by chance. Measured in a
population, not in a family, and often varies in
different populations.
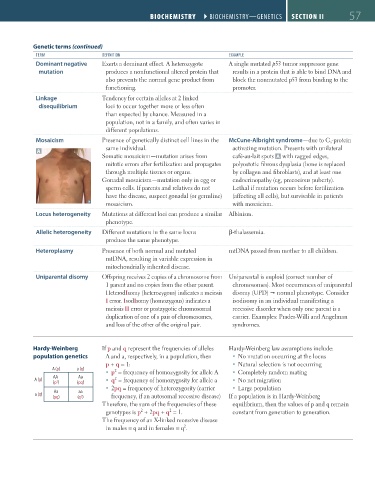
Mosaicism Presence of genetically distinct cell lines in the McCune-Albright syndrome—due to G s -protein
A same individual. activating mutation. Presents with unilateral
Somatic mosaicism—mutation arises from café-au-lait spots A with ragged edges,
mitotic errors after fertilization and propagates polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (bone is replaced
through multiple tissues or organs. by collagen and fibroblasts), and at least one
Gonadal mosaicism—mutation only in egg or endocrinopathy (eg, precocious puberty).
sperm cells. If parents and relatives do not Lethal if mutation occurs before fertilization
have the disease, suspect gonadal (or germline) (affecting all cells), but survivable in patients
mosaicism. with mosaicism.
Locus heterogeneity Mutations at different loci can produce a similar Albinism.
phenotype.
Allelic heterogeneity Different mutations in the same locus β-thalassemia.
produce the same phenotype.
Heteroplasmy Presence of both normal and mutated mtDNA passed from mother to all children.
mtDNA, resulting in variable expression in
mitochondrially inherited disease.
Uniparental disomy Offspring receives 2 copies of a chromosome from Uniparental is euploid (correct number of
1 parent and no copies from the other parent. chromosomes). Most occurrences of uniparental
HeterodIsomy (heterozygous) indicates a meiosis disomy (UPD) normal phenotype. Consider
I error. IsodIsomy (homozygous) indicates a isodisomy in an individual manifesting a
meiosis II error or postzygotic chromosomal recessive disorder when only one parent is a
duplication of one of a pair of chromosomes, carrier. Examples: Prader-Willi and Angelman
and loss of the other of the original pair. syndromes.
Hardy-Weinberg If p and q represent the frequencies of alleles Hardy-Weinberg law assumptions include:
population genetics A and a, respectively, in a population, then No mutation occurring at the locus
p + q = 1: Natural selection is not occurring
A (p) a (q) 2
p = frequency of homozygosity for allele A Completely random mating
AA Aa
2
A (p) q = frequency of homozygosity for allele a No net migration
(p ) (pq)
2pq = frequency of heterozygosity (carrier Large population
Aa aa
a (q) frequency, if an autosomal recessive disease) If a population is in Hardy-Weinberg
(pq) (q )
Therefore, the sum of the frequencies of these equilibrium, then the values of p and q remain
2
2
genotypes is p + 2pq + q = 1. constant from generation to generation.
The frequency of an X-linked recessive disease
2
in males = q and in females = q .
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 57 11/7/19 3:16 PM