Page 104 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 104
60 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—GENETICS
Autosomal dominant Achondroplasia, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, familial adenomatous polyposis,
diseases familial hypercholesterolemia, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu
syndrome), hereditary spherocytosis, Huntington disease, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Marfan syndrome,
multiple endocrine neoplasias, myotonic muscular dystrophy, neurofibromatosis type 1 (von
Recklinghausen disease), neurofibromatosis type 2, tuberous sclerosis, von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Autosomal recessive Oculocutaneous albinism, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), cystic
diseases fibrosis, Friedreich ataxia, glycogen storage diseases, hemochromatosis, Kartagener syndrome,
mucopolysaccharidoses (except Hunter syndrome), phenylketonuria, sickle cell anemia,
sphingolipidoses (except Fabry disease), thalassemias, Wilson disease.
Cystic fibrosis
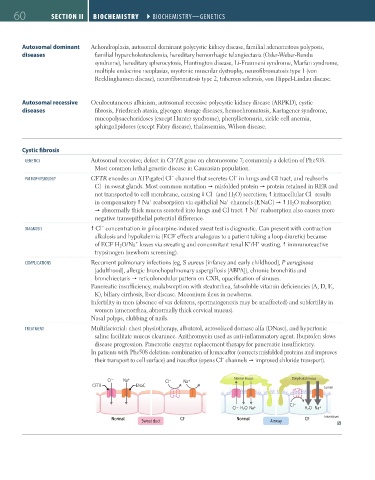
GENETICS Autosomal recessive; defect in CFTR gene on chromosome 7; commonly a deletion of Phe508.
Most common lethal genetic disease in Caucasian population.
−
−
PATHOPHYSIOlOGY CFTR encodes an ATP-gated Cl channel that secretes Cl in lungs and GI tract, and reabsorbs
−
Cl in sweat glands. Most common mutation misfolded protein protein retained in RER and
−
−
not transported to cell membrane, causing Cl (and H 2 O) secretion; intracellular Cl results
in compensatory Na reabsorption via epithelial Na channels (ENaC) H 2 O reabsorption
+
+
+
abnormally thick mucus secreted into lungs and GI tract. Na reabsorption also causes more
negative transepithelial potential difference.
−
DIAGNOSIS Cl concentration in pilocarpine-induced sweat test is diagnostic. Can present with contraction
alkalosis and hypokalemia (ECF effects analogous to a patient taking a loop diuretic) because
+
+
+
of ECF H 2 O/Na losses via sweating and concomitant renal K /H wasting. immunoreactive
trypsinogen (newborn screening).
COMPlICATIONS Recurrent pulmonary infections (eg, S aureus [infancy and early childhood], P aeruginosa
[adulthood], allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis [ABPA]), chronic bronchitis and
bronchiectasis reticulonodular pattern on CXR, opacification of sinuses.
Pancreatic insufficiency, malabsorption with steatorrhea, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies (A, D, E,
K), biliary cirrhosis, liver disease. Meconium ileus in newborns.
Infertility in men (absence of vas deferens, spermatogenesis may be unaffected) and subfertility in
women (amenorrhea, abnormally thick cervical mucus).
Nasal polyps, clubbing of nails.
TREATMENT Multifactorial: chest physiotherapy, albuterol, aerosolized dornase alfa (DNase), and hypertonic
saline facilitate mucus clearance. Azithromycin used as anti-inflammatory agent. Ibuprofen slows
disease progression. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for pancreatic insufficiency.
In patients with Phe508 deletion: combination of lumacaftor (corrects misfolded proteins and improves
–
their transport to cell surface) and ivacaftor (opens Cl channels improved chloride transport).
CI – Na + CI – Na + Normal mucus Dehydrated mucus
CFTR ENaC Lumen
CI – H₂O Na + CI – H₂O Na +
Normal CF Normal CF Interstitium
Sweat duct Airway
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 60 11/7/19 3:16 PM