Page 99 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 99
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES SECTION II 55
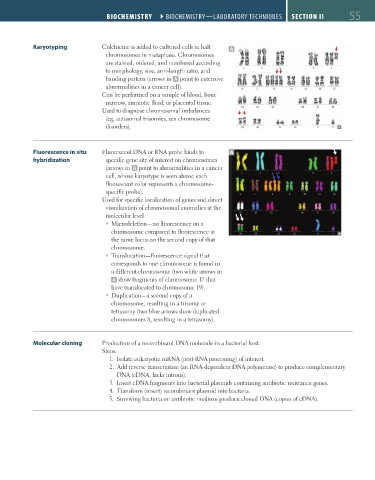
Karyotyping Colchicine is added to cultured cells to halt A
chromosomes in metaphase. Chromosomes
are stained, ordered, and numbered according
to morphology, size, arm-length ratio, and
banding pattern (arrows in A point to extensive
abnormalities in a cancer cell).
Can be performed on a sample of blood, bone
marrow, amniotic fluid, or placental tissue.
Used to diagnose chromosomal imbalances
(eg, autosomal trisomies, sex chromosome
disorders).
Fluorescence in situ Fluorescent DNA or RNA probe binds to A
hybridization specific gene site of interest on chromosomes
(arrows in A point to abnormalities in a cancer
cell, whose karyotype is seen above; each
fluorescent color represents a chromosome-
specific probe).
Used for specific localization of genes and direct
visualization of chromosomal anomalies at the
molecular level.
Microdeletion—no fluorescence on a
chromosome compared to fluorescence at
the same locus on the second copy of that
chromosome.
Translocation—fluorescence signal that
corresponds to one chromosome is found in
a different chromosome (two white arrows in
A show fragments of chromosome 17 that
have translocated to chromosome 19).
Duplication—a second copy of a
chromosome, resulting in a trisomy or
tetrasomy (two blue arrows show duplicated
chromosomes 8, resulting in a tetrasomy).
Molecular cloning Production of a recombinant DNA molecule in a bacterial host.
Steps:
1. Isolate eukaryotic mRNA (post-RNA processing) of interest.
2. Add reverse transcriptase (an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase) to produce complementary
DNA (cDNA, lacks introns).
3. Insert cDNA fragments into bacterial plasmids containing antibiotic resistance genes.
4. Transform (insert) recombinant plasmid into bacteria.
5. Surviving bacteria on antibiotic medium produce cloned DNA (copies of cDNA).
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 55 11/7/19 3:16 PM