Page 185 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 185
Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology SEcTioN ii 141
Leprosy Also called Hansen disease. Caused by Mycobacterium leprae, an acid-fast bacillus that likes cool
temperatures (infects skin and superficial nerves—“glove and stocking” loss of sensation A ) and
A
cannot be grown in vitro. Diagnosed via skin biopsy or tissue PCR. Reservoir in United States:
armadillos.
Leprosy has 2 forms (many cases fall temporarily between two extremes):
Lepromatous—presents diffusely over the skin, with Leonine (Lion-like) facies B , and is
communicable (high bacterial load); characterized by low cell-mediated immunity with a
largely Th2 response. Lepromatous form can be Lethal.
B
Tuberculoid—limited to a few hypoesthetic, hairless skin plaques; characterized by high cell-
mediated immunity with a largely Th1-type response and low bacterial load.
Treatment: dapsone and rifampin for tuberculoid form; clofazimine is added for lepromatous form.
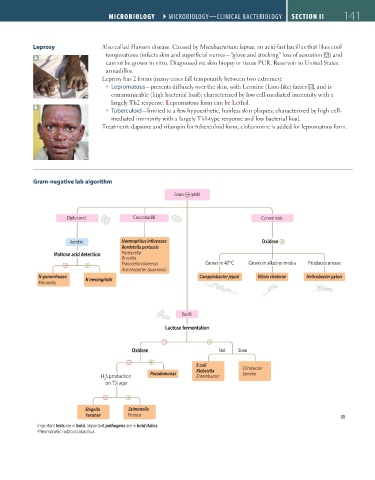
Gram-negative lab algorithm
Gram (pink)
Diplococci Coccobacilli Curved rods
Aerobic Haemophilus influenzae Oxidase
Bordetella pertussis
Maltose acid detection Pasteurella
Brucella
Francisella tularensis Grows in 42°C Grows in alkaline media Produces urease
Acinetobacter baumannii
N gonorrhoeae N meningitidis Campylobacter jejuni Vibrio cholerae Helicobacter pylori
Moraxella
Bacilli
Lactose fermentation
Oxidase Fast Slow
E coli
Klebsiella Citrobacter
Pseudomonas Serratia
H S production Enterobacter
2
on TSI agar
Shigella Salmonella
Yersinia a Proteus
Important tests are in bold. Important pathogens are in bold italics.
a Pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 141 11/14/19 12:20 PM