Page 183 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 183
Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology SEcTioN ii 139
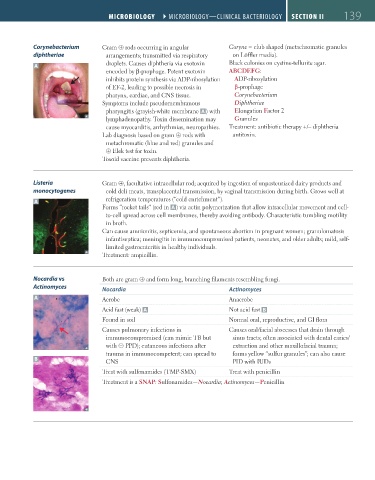
Corynebacterium Gram ⊕ rods occurring in angular Coryne = club shaped (metachromatic granules
diphtheriae arrangements; transmitted via respiratory on Löffler media).
A droplets. Causes diphtheria via exotoxin Black colonies on cystine-tellurite agar.
encoded by β-prophage. Potent exotoxin ABCDEFG:
inhibits protein synthesis via ADP-ribosylation ADP-ribosylation
of EF-2, leading to possible necrosis in β-prophage
pharynx, cardiac, and CNS tissue. Corynebacterium
Symptoms include pseudomembranous Diphtheriae
pharyngitis (grayish-white membrane A ) with Elongation Factor 2
lymphadenopathy. Toxin dissemination may Granules
cause myocarditis, arrhythmias, neuropathies. Treatment: antibiotic therapy +/– diphtheria
Lab diagnosis based on gram ⊕ rods with antitoxin.
metachromatic (blue and red) granules and
⊕ Elek test for toxin.
Toxoid vaccine prevents diphtheria.
Listeria Gram ⊕, facultative intracellular rod; acquired by ingestion of unpasteurized dairy products and
monocytogenes cold deli meats, transplacental transmission, by vaginal transmission during birth. Grows well at
A refrigeration temperatures (“cold enrichment”).
Forms “rocket tails” (red in A ) via actin polymerization that allow intracellular movement and cell-
to-cell spread across cell membranes, thereby avoiding antibody. Characteristic tumbling motility
in broth.
Can cause amnionitis, septicemia, and spontaneous abortion in pregnant women; granulomatosis
infantiseptica; meningitis in immunocompromised patients, neonates, and older adults; mild, self-
limited gastroenteritis in healthy individuals.
Treatment: ampicillin.
Nocardia vs Both are gram ⊕ and form long, branching filaments resembling fungi.
Actinomyces Nocardia Actinomyces
A Aerobe Anaerobe
Acid fast (weak) A Not acid fast B
Found in soil Normal oral, reproductive, and GI flora
Causes pulmonary infections in Causes oral/facial abscesses that drain through
immunocompromised (can mimic TB but sinus tracts; often associated with dental caries/
with ⊝ PPD); cutaneous infections after extraction and other maxillofacial trauma;
trauma in immunocompetent; can spread to forms yellow “sulfur granules”; can also cause
B CNS PID with IUDs
Treat with sulfonamides (TMP-SMX) Treat with penicillin
Treatment is a SNAP: Sulfonamides—Nocardia; Actinomyces—Penicillin
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 139 11/14/19 12:20 PM