Page 186 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 186
142 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology
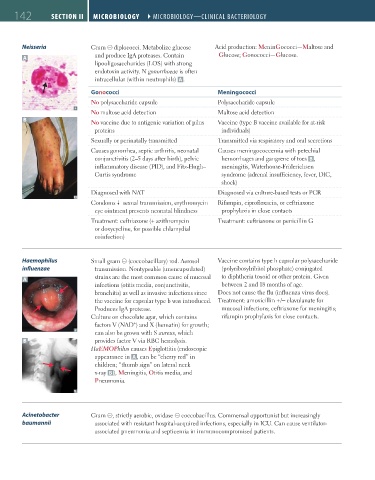
Neisseria Gram ⊝ diplococci. Metabolize glucose Acid production: MeninGococci—Maltose and
A and produce IgA proteases. Contain Glucose; Gonococci—Glucose.
lipooligosaccharides (LOS) with strong
endotoxin activity. N gonorrhoeae is often
intracellular (within neutrophils) A .
Gonococci Meningococci
No polysaccharide capsule Polysaccharide capsule
No maltose acid detection Maltose acid detection
B No vaccine due to antigenic variation of pilus Vaccine (type B vaccine available for at-risk
proteins individuals)
Sexually or perinatally transmitted Transmitted via respiratory and oral secretions
Causes gonorrhea, septic arthritis, neonatal Causes meningococcemia with petechial
conjunctivitis (2–5 days after birth), pelvic hemorrhages and gangrene of toes B ,
inflammatory disease (PID), and Fitz-Hugh– meningitis, Waterhouse-Friderichsen
Curtis syndrome syndrome (adrenal insufficiency, fever, DIC,
shock)
Diagnosed with NAT Diagnosed via culture-based tests or PCR
Condoms sexual transmission, erythromycin Rifampin, ciprofloxacin, or ceftriaxone
eye ointment prevents neonatal blindness prophylaxis in close contacts
Treatment: ceftriaxone (+ azithromycin Treatment: ceftriaxone or penicillin G
or doxycycline, for possible chlamydial
coinfection)
Haemophilus Small gram ⊝ (coccobacillary) rod. Aerosol Vaccine contains type b capsular polysaccharide
influenzae transmission. Nontypeable (unencapsulated) (polyribosylribitol phosphate) conjugated
A strains are the most common cause of mucosal to diphtheria toxoid or other protein. Given
infections (otitis media, conjunctivitis, between 2 and 18 months of age.
bronchitis) as well as invasive infections since Does not cause the flu (influenza virus does).
the vaccine for capsular type b was introduced. Treatment: amoxicillin +/− clavulanate for
Produces IgA protease. mucosal infections; ceftriaxone for meningitis;
Culture on chocolate agar, which contains rifampin prophylaxis for close contacts.
+
factors V (NAD ) and X (hematin) for growth;
can also be grown with S aureus, which
B provides factor V via RBC hemolysis.
HaEMOPhilus causes Epiglottitis (endoscopic
appearance in A , can be “cherry red” in
children; “thumb sign” on lateral neck
x-ray B ), Meningitis, Otitis media, and
Pneumonia.
Acinetobacter Gram ⊝, strictly aerobic, oxidase ⊝ coccobacillus. Commensal opportunist but increasingly
baumannii associated with resistant hospital-acquired infections, especially in ICU. Can cause ventilator-
associated pneumonia and septicemia in immunocompromised patients.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 142 11/14/19 12:20 PM