Page 188 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 188
144 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology
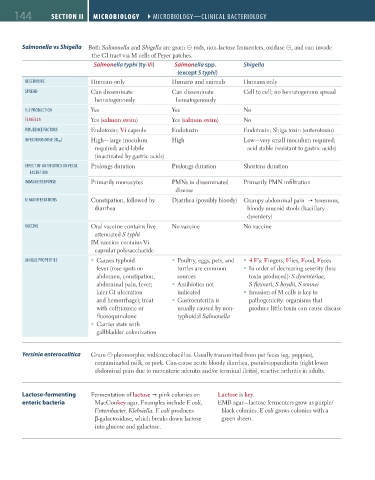
Salmonella vs Shigella Both Salmonella and Shigella are gram ⊝ rods, non-lactose fermenters, oxidase ⊝, and can invade
the GI tract via M cells of Peyer patches.
Salmonella typhi (ty-Vi) Salmonella spp. Shigella
(except S typhi)
reserVoirs Humans only Humans and animals Humans only
sPreaD Can disseminate Can disseminate Cell to cell; no hematogenous spread
hematogenously hematogenously
H 2 s ProDUctioN Yes Yes No
Flagella Yes (salmon swim) Yes (salmon swim) No
VirUleNce Factors Endotoxin; Vi capsule Endotoxin Endotoxin; Shiga toxin (enterotoxin)
iNFectioUs Dose (iD 50 ) High—large inoculum High Low—very small inoculum required;
required; acid-labile acid stable (resistant to gastric acids)
(inactivated by gastric acids)
eFFect oF aNtibiotics oN Fecal Prolongs duration Prolongs duration Shortens duration
eXcretioN
immUNe resPoNse Primarily monocytes PMNs in disseminated Primarily PMN infiltration
disease
gi maNiFestatioNs Constipation, followed by Diarrhea (possibly bloody) Crampy abdominal pain tenesmus,
diarrhea bloody mucoid stools (bacillary
dysentery)
VacciNe Oral vaccine contains live No vaccine No vaccine
attenuated S typhi
IM vaccine contains Vi
capsular polysaccharide
UNiQUe ProPerties Causes typhoid Poultry, eggs, pets, and 4 F’s: Fingers, Flies, Food, Feces
fever (rose spots on turtles are common In order of decreasing severity (less
abdomen, constipation, sources toxin produced): S dysenteriae,
abdominal pain, fever; Antibiotics not S flexneri, S boydii, S sonnei
later GI ulceration indicated Invasion of M cells is key to
and hemorrhage); treat Gastroenteritis is pathogenicity: organisms that
with ceftriaxone or usually caused by non- produce little toxin can cause disease
fluoroquinolone typhoidal Salmonella
Carrier state with
gallbladder colonization
Yersinia enterocolitica Gram ⊝ pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus. Usually transmitted from pet feces (eg, puppies),
contaminated milk, or pork. Can cause acute bloody diarrhea, pseudoappendicitis (right lower
abdominal pain due to mesenteric adenitis and/or terminal ileitis), reactive arthritis in adults.
Lactose-fermenting Fermentation of lactose pink colonies on Lactose is key.
enteric bacteria MacConkey agar. Examples include E coli, EMB agar—lactose fermenters grow as purple/
Enterobacter, Klebsiella. E coli produces black colonies. E coli grows colonies with a
β-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose green sheen.
into glucose and galactose.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 144 11/14/19 12:20 PM