Page 336 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 336
292 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY
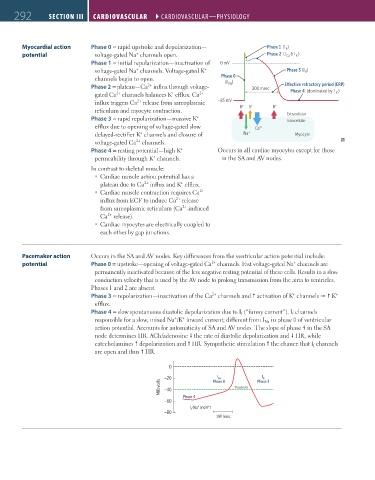
Myocardial action Phase 0 = rapid upstroke and depolarization— Phase 1 (I )
K
+
potential voltage-gated Na channels open. Phase 2 (I Ca & I )
K
Phase 1 = initial repolarization—inactivation of 0 mV
+
+
voltage-gated Na channels. Voltage-gated K Phase 3 (I )
K
channels begin to open. Phase 0
Na
2+
Phase 2 = plateau—Ca influx through voltage- (I ) 200 msec E ective refractory period (ERP)
2+
K
+
gated Ca channels balances K efflux. Ca 2+ Phase 4 (dominated by I )
2+
influx triggers Ca release from sarcoplasmic –85 mV + + +
reticulum and myocyte contraction. K K K
+
Phase 3 = rapid repolarization—massive K Extracellular
Intracellular
efflux due to opening of voltage-gated slow Ca 2+
+
delayed-rectifier K channels and closure of Na + Myocyte
2+
voltage-gated Ca channels.
+
Phase 4 = resting potential—high K Occurs in all cardiac myocytes except for those
+
permeability through K channels. in the SA and AV nodes.
In contrast to skeletal muscle:
Cardiac muscle action potential has a
2+
+
plateau due to Ca influx and K efflux.
Cardiac muscle contraction requires Ca
2+
2+
influx from ECF to induce Ca release
2+
from sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca -induced
2+
Ca release).
Cardiac myocytes are electrically coupled to
each other by gap junctions.
Pacemaker action Occurs in the SA and AV nodes. Key differences from the ventricular action potential include:
+
2+
potential Phase 0 = upstroke—opening of voltage-gated Ca channels. Fast voltage-gated Na channels are
permanently inactivated because of the less negative resting potential of these cells. Results in a slow
conduction velocity that is used by the AV node to prolong transmission from the atria to ventricles.
Phases 1 and 2 are absent.
+
+
2+
Phase 3 = repolarization—inactivation of the Ca channels and activation of K channels K
efflux.
Phase 4 = slow spontaneous diastolic depolarization due to I f (“funny current”). I f channels
+
+
responsible for a slow, mixed Na /K inward current; different from I Na in phase 0 of ventricular
action potential. Accounts for automaticity of SA and AV nodes. The slope of phase 4 in the SA
node determines HR. ACh/adenosine the rate of diastolic depolarization and HR, while
catecholamines depolarization and HR. Sympathetic stimulation the chance that I f channels
are open and thus HR.
0
I
I
–20 Phase 0 Phase 3
Ca
K
Millivolts –40 Threshold
Phase 4
–60
I (Na and K ) +
+
f
–80
100 msec
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 292 11/7/19 4:24 PM