Page 340 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 340
296 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY
Atrial natriuretic Released from atrial myocytes in response to blood volume and atrial pressure. Acts via cGMP.
+
peptide Causes vasodilation and Na reabsorption at the renal collecting tubule. Dilates afferent renal
arterioles and constricts efferent arterioles, promoting diuresis and contributing to “aldosterone
escape” mechanism.
B-type (brain) Released from ventricular myocytes in response to tension. Similar physiologic action to ANP,
natriuretic peptide with longer half-life. BNP blood test used for diagnosing HF (very good negative predictive value).
Available in recombinant form (nesiritide) for treatment of HF.
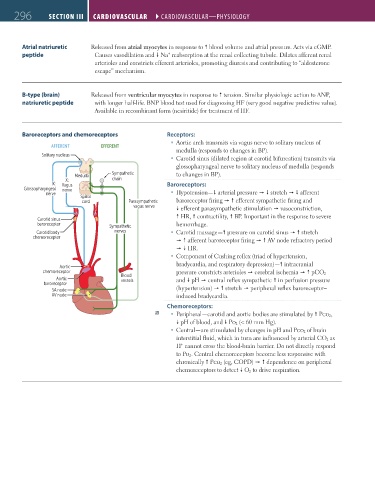
Baroreceptors and chemoreceptors Receptors:
Aortic arch transmits via vagus nerve to solitary nucleus of
AFFERENT EFFERENT
medulla (responds to changes in BP).
Solitary nucleus
Carotid sinus (dilated region at carotid bifurcation) transmits via
glossopharyngeal nerve to solitary nucleus of medulla (responds
Sympathetic to changes in BP).
Medulla
Medulla
X: X: chain
IX: IX: Vagus Baroreceptors:
Vagus
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Glossopharyngeal
nerve
nerve Hypotension— arterial pressure stretch afferent
nerve
Spinal
Spinal
cordcord Parasympathetic baroreceptor firing efferent sympathetic firing and
vagus nerve efferent parasympathetic stimulation vasoconstriction,
HR, contractility, BP. Important in the response to severe
Carotid sinus
baroreceptor Sympathetic hemorrhage.
Carotid body nerves Carotid massage— pressure on carotid sinus stretch
chemoreceptor
afferent baroreceptor firing AV node refractory period
HR.
Component of Cushing reflex (triad of hypertension,
bradycardia, and respiratory depression)— intracranial
Aortic
chemoreceptor Blood pressure constricts arterioles cerebral ischemia pCO 2
Aortic vessels and pH central reflex sympathetic in perfusion pressure
baroreceptor
SA node (hypertension) stretch peripheral reflex baroreceptor–
AV node induced bradycardia.
Chemoreceptors:
Peripheral—carotid and aortic bodies are stimulated by Pco 2 ,
pH of blood, and Po 2 (< 60 mm Hg).
Central—are stimulated by changes in pH and Pco 2 of brain
interstitial fluid, which in turn are influenced by arterial CO 2 as
+
H cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. Do not directly respond
to Po 2 . Central chemoreceptors become less responsive with
chronically Pco 2 (eg, COPD) dependence on peripheral
chemoreceptors to detect O 2 to drive respiration.
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 296 11/7/19 4:24 PM