Page 341 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 341
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY SECTION III 297
Normal cardiac Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP; 130/90
pressures in mm Hg) is a good approximation of left 25/10
atrial pressure. In mitral stenosis, PCWP > <12 4 12 PCWP
LV end diastolic pressure. PCWP is measured
with pulmonary artery catheter (Swan-Ganz <5 130/10
catheter). 25/5
Autoregulation How blood flow to an organ remains constant over a wide range of perfusion pressures.
ORGAN FACTORS dETERMINING AuTOREGulATION
Heart Local metabolites (vasodilatory): adenosine, The pulmonary vasculature is unique in that
alveolar hypoxia causes vasoconstriction so
NO, CO 2 , O 2
Brain Local metabolites (vasodilatory): CO 2 (pH) that only well-ventilated areas are perfused. In
other organs, hypoxia causes vasodilation.
Kidneys Myogenic and tubuloglomerular feedback
Lungs Hypoxia causes vasoconstriction
Skeletal muscle Local metabolites during exercise (vasodilatory): CHALK
+
CO 2 , H , Adenosine, Lactate, K +
At rest: sympathetic tone in arteries
Skin Sympathetic vasoconstriction most important
mechanism for temperature control
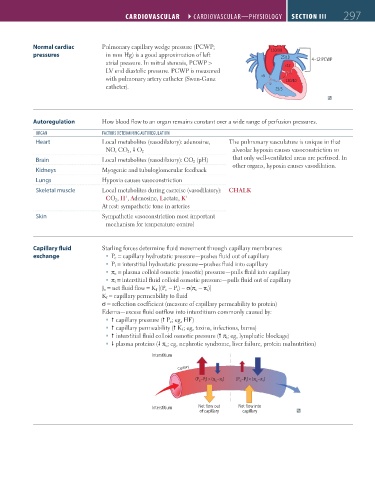
Capillary fluid Starling forces determine fluid movement through capillary membranes:
exchange P c = capillary hydrostatic pressure—pushes fluid out of capillary
P i = interstitial hydrostatic pressure—pushes fluid into capillary
π c = plasma colloid osmotic (oncotic) pressure—pulls fluid into capillary
π i = interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure—pulls fluid out of capillary
J v = net fluid flow = K f [(P c − P i ) − σ(π c − π i )]
K f = capillary permeability to fluid
σ = reflection coefficient (measure of capillary permeability to protein)
Edema—excess fluid outflow into interstitium commonly caused by:
capillary pressure ( P c ; eg, HF)
capillary permeability ( K f ; eg, toxins, infections, burns)
interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure ( π i ; eg, lymphatic blockage)
plasma proteins ( π c ; eg, nephrotic syndrome, liver failure, protein malnutrition)
Interstitium
Capillary
(P –P) > (π –π ) i (P c –P) < (π –π ) i
c
c
i
c
i
Interstitium Net flow out Net flow into
of capillary capillary
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 297 11/7/19 4:24 PM