Page 339 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 339
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY SECTION III 295
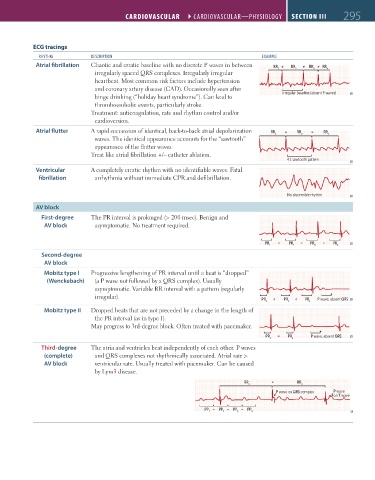
ECG tracings
RHYTHM dESCRIPTION EXAMPlE
Atrial fibrillation Chaotic and erratic baseline with no discrete P waves in between RR ≠ RR ≠ RR ≠ RR
irregularly spaced QRS complexes. Irregularly irregular 1 2 3 4
heartbeat. Most common risk factors include hypertension
and coronary artery disease (CAD). Occasionally seen after
binge drinking (“holiday heart syndrome”). Can lead to Irregular baseline (absent P waves)
thromboembolic events, particularly stroke.
Treatment: anticoagulation, rate and rhythm control and/or
cardioversion.
Atrial flutter A rapid succession of identical, back-to-back atrial depolarization RR = RR = RR
waves. The identical appearance accounts for the “sawtooth” 1 2 3
appearance of the flutter waves.
Treat like atrial fibrillation +/– catheter ablation.
4:1 sawtooth pattern
Ventricular A completely erratic rhythm with no identifiable waves. Fatal
fibrillation arrhythmia without immediate CPR and defibrillation.
No discernible rhythm
AV block
First-degree The PR interval is prolonged (> 200 msec). Benign and
AV block asymptomatic. No treatment required.
PR 1 = PR 2 = PR 3 = PR 4
Second-degree
AV block
Mobitz type I Progressive lengthening of PR interval until a beat is “dropped”
(Wenckebach) (a P wave not followed by a QRS complex). Usually
asymptomatic. Variable RR interval with a pattern (regularly
irregular).
PR
1 < PR 1 < PR 2 < PR 3 P wave, absent QRS
Mobitz type II Dropped beats that are not preceded by a change in the length of
the PR interval (as in type I).
May progress to 3rd-degree block. Often treated with pacemaker.
PR 1 = PR 1 = PR 2 P wave, absent QRS
Third-degree The atria and ventricles beat independently of each other. P waves
(complete) and QRS complexes not rhythmically associated. Atrial rate >
AV block ventricular rate. Usually treated with pacemaker. Can be caused
by Lym3 disease.
RR 1 = RR 2
P wave on QRS complex P wave
on T wave
PP = PP 2 = PP 3 = PP 4
1
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 295 11/7/19 4:24 PM