Page 342 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 342
298 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY
` `CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY
Congenital heart diseases
RIGHT-TO-lEFT SHuNTS Early cyanosis—“blue babies.” Often diagnosed The 5 T’s:
prenatally or become evident immediately 1. Truncus arteriosus (1 vessel)
after birth. Usually require urgent surgical 2. Transposition (2 switched vessels)
treatment and/or maintenance of a PDA. 3. Tricuspid atresia (3 = Tri)
4. Tetralogy of Fallot (4 = Tetra)
5. TAPVR (5 letters in the name)
Persistent truncus Truncus arteriosus fails to divide into
arteriosus pulmonary trunk and aorta due to failure of
aorticopulmonary septum formation; most
patients have accompanying VSD.
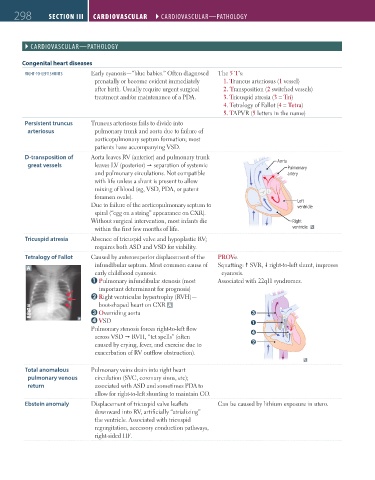
D-transposition of Aorta leaves RV (anterior) and pulmonary trunk
great vessels leaves LV (posterior) separation of systemic Aorta Pulmonary
and pulmonary circulations. Not compatible artery
with life unless a shunt is present to allow
mixing of blood (eg, VSD, PDA, or patent
foramen ovale).
Due to failure of the aorticopulmonary septum to Left
ventricle
spiral (“egg on a string” appearance on CXR).
Without surgical intervention, most infants die Right
within the first few months of life. ventricle
Tricuspid atresia Absence of tricuspid valve and hypoplastic RV;
requires both ASD and VSD for viability.
Tetralogy of Fallot Caused by anterosuperior displacement of the PROVe.
infundibular septum. Most common cause of Squatting: SVR, right-to-left shunt, improves
A
early childhood cyanosis. cyanosis.
Pulmonary infundibular stenosis (most Associated with 22q11 syndromes.
important determinant for prognosis)
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH)—
boot-shaped heart on CXR A
Overriding aorta S
VSD Q
Pulmonary stenosis forces right-to-left flow
across VSD RVH, “tet spells” (often T
caused by crying, fever, and exercise due to R
exacerbation of RV outflow obstruction).
Total anomalous Pulmonary veins drain into right heart
pulmonary venous circulation (SVC, coronary sinus, etc);
return associated with ASD and sometimes PDA to
allow for right-to-left shunting to maintain CO.
Ebstein anomaly Displacement of tricuspid valve leaflets Can be caused by lithium exposure in utero.
downward into RV, artificially “atrializing”
the ventricle. Associated with tricuspid
regurgitation, accessory conduction pathways,
right-sided HF.
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 298 11/7/19 4:24 PM