Page 349 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 349
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY SECTION III 305
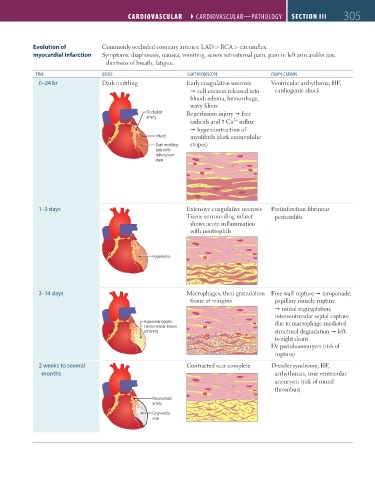
Evolution of Commonly occluded coronary arteries: LAD > RCA > circumflex.
myocardial infarction Symptoms: diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, severe retrosternal pain, pain in left arm and/or jaw,
shortness of breath, fatigue.
TIME GROSS lIGHT MICROSCOPE COMPlICATIONS
0–24 hr Dark mottling Early coagulative necrosis Ventricular arrhythmia, HF,
cell content released into cardiogenic shock
blood; edema, hemorrhage,
wavy fibers
Occluded Reperfusion injury free
artery
2+
radicals and Ca influx
hypercontraction of
Infarct myofibrils (dark eosinophilic
Dark mottling; stripes)
pale with
tetrazolium
stain
1–3 days Extensive coagulative necrosis Postinfarction fibrinous
Tissue surrounding infarct pericarditis
shows acute inflammation
with neutrophils
Hyperemia
3–14 days Macrophages, then granulation Free wall rupture tamponade;
tissue at margins papillary muscle rupture
mitral regurgitation;
interventricular septal rupture
Hyperemic border; due to macrophage-mediated
central yellow-brown
softening structural degradation left-
to-right shunt
LV pseudoaneurysm (risk of
rupture)
2 weeks to several Contracted scar complete Dressler syndrome, HF,
months arrhythmias, true ventricular
aneurysm (risk of mural
thrombus)
Recanalized
artery
Gray-white
scar
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 305 11/7/19 4:24 PM