Page 479 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 479
Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—PhaRmacology SectIon III 435
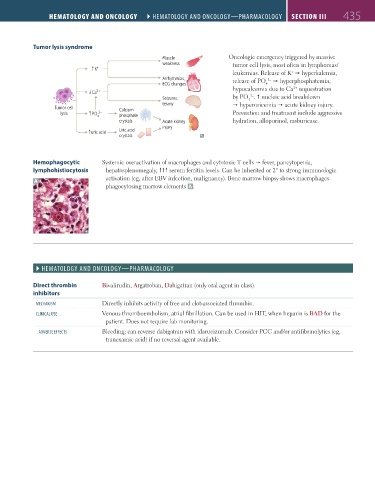
Tumor lysis syndrome
Muscle Oncologic emergency triggered by massive
weakness tumor cell lysis, most often in lymphomas/
K ↓ +
leukemias. Release of K hyperkalemia,
+
Arrhythmias, release of PO hyperphosphatemia,
3–
ECG changes 4 2+
↓ Ca 2+ hypocalcemia due to Ca sequestration
3–
Seizures, by PO . nucleic acid breakdown
4
tetany hyperuricemia acute kidney injury.
Tumor cell Calcium
lysis ↓ PO 3– Prevention and treatment include aggressive
4 phosphate
crystals Acute kidney hydration, allopurinol, rasburicase.
injury
Uric acid
uric acid
crystals
↓
Hemophagocytic Systemic overactivation of macrophages and cytotoxic T cells fever, pancytopenia,
lymphohistiocytosis hepatosplenomegaly, serum ferritin levels. Can be inherited or 2° to strong immunologic
A activation (eg, after EBV infection, malignancy). Bone marrow biopsy shows macrophages
phagocytosing marrow elements A .
` hematology and oncology—PhaRmacology
Direct thrombin Bivalirudin, Argatroban, Dabigatran (only oral agent in class).
inhibitors
mechanISm Directly inhibits activity of free and clot-associated thrombin.
clInIcal USe Venous thromboembolism, atrial fibrillation. Can be used in HIT, when heparin is BAD for the
patient. Does not require lab monitoring.
adVeRSe eFFectS Bleeding; can reverse dabigatran with idarucizumab. Consider PCC and/or antifibrinolytics (eg,
tranexamic acid) if no reversal agent available.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 435 11/7/19 5:05 PM