Page 640 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 640
596 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy
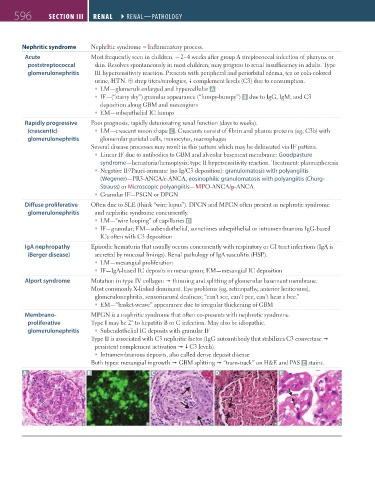
Nephritic syndrome NephrItic syndrome = Inflammatory process.
Acute Most frequently seen in children. ~ 2–4 weeks after group A streptococcal infection of pharynx or
poststreptococcal skin. Resolves spontaneously in most children; may progress to renal insufficiency in adults. Type
glomerulonephritis III hypersensitivity reaction. Presents with peripheral and periorbital edema, tea or cola-colored
urine, HTN. ⊕ strep titers/serologies, complement levels (C3) due to consumption.
LM—glomeruli enlarged and hypercellular A
IF—(“starry sky”) granular appearance (“lumpy-bumpy”) B due to IgG, IgM, and C3
deposition along GBM and mesangium
EM—subepithelial IC humps
Rapidly progressive Poor prognosis, rapidly deteriorating renal function (days to weeks).
(crescentic) LM—crescent moon shape C . Crescents consist of fibrin and plasma proteins (eg, C3b) with
glomerulonephritis glomerular parietal cells, monocytes, macrophages
Several disease processes may result in this pattern which may be delineated via IF pattern.
Linear IF due to antibodies to GBM and alveolar basement membrane: Goodpasture
syndrome—hematuria/hemoptysis; type II hypersensitivity reaction. Treatment: plasmapheresis
Negative IF/Pauci-immune (no Ig/C3 deposition): granulomatosis with polyangiitis
(Wegener)—PR3-ANCA/c-ANCA, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-
Strauss) or Microscopic polyangiitis—MPO-ANCA/p-ANCA
Granular IF—PSGN or DPGN
Diffuse proliferative Often due to SLE (think “wire lupus”). DPGN and MPGN often present as nephrotic syndrome
glomerulonephritis and nephritic syndrome concurrently.
LM—“wire looping” of capillaries D
IF—granular; EM—subendothelial, sometimes subepithelial or intramembranous IgG-based
ICs often with C3 deposition
IgA nephropathy Episodic hematuria that usually occurs concurrently with respiratory or GI tract infections (IgA is
(Berger disease) secreted by mucosal linings). Renal pathology of IgA vasculitis (HSP).
LM—mesangial proliferation
IF—IgA-based IC deposits in mesangium; EM—mesangial IC deposition
Alport syndrome Mutation in type IV collagen thinning and splitting of glomerular basement membrane.
Most commonly X-linked dominant. Eye problems (eg, retinopathy, anterior lenticonus),
glomerulonephritis, sensorineural deafness; “can’t see, can’t pee, can’t hear a bee.”
EM—“basket-weave” appearance due to irregular thickening of GBM
Membrano- MPGN is a nephritic syndrome that often co-presents with nephrotic syndrome.
proliferative Type I may be 2° to hepatitis B or C infection. May also be idiopathic.
glomerulonephritis Subendothelial IC deposits with granular IF
Type II is associated with C3 nephritic factor (IgG autoantibody that stabilizes C3 convertase
persistent complement activation C3 levels).
Intramembranous deposits, also called dense deposit disease
Both types: mesangial ingrowth GBM splitting “tram-track” on H&E and PAS E stains.
A B C D E
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 596 11/7/19 5:42 PM