Page 643 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 643
Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy SeCTIOn III 599
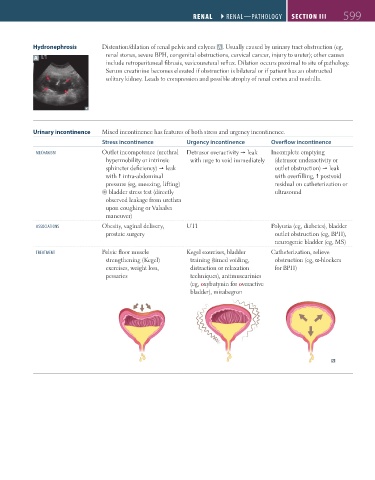
Hydronephrosis Distention/dilation of renal pelvis and calyces A . Usually caused by urinary tract obstruction (eg,
renal stones, severe BPH, congenital obstructions, cervical cancer, injury to ureter); other causes
A
include retroperitoneal fibrosis, vesicoureteral reflux. Dilation occurs proximal to site of pathology.
Serum creatinine becomes elevated if obstruction is bilateral or if patient has an obstructed
solitary kidney. Leads to compression and possible atrophy of renal cortex and medulla.
Urinary incontinence Mixed incontinence has features of both stress and urgency incontinence.
Stress incontinence Urgency incontinence Overflow incontinence
mEChANism Outlet incompetence (urethral Detrusor overactivity leak Incomplete emptying
hypermobility or intrinsic with urge to void immediately (detrusor underactivity or
sphincter deficiency) leak outlet obstruction) leak
with intra-abdominal with overfilling, postvoid
pressure (eg, sneezing, lifting) residual on catheterization or
⊕ bladder stress test (directly ultrasound
observed leakage from urethra
upon coughing or Valsalva
maneuver)
AssoCiAtioNs Obesity, vaginal delivery, UTI Polyuria (eg, diabetes), bladder
prostate surgery outlet obstruction (eg, BPH),
neurogenic bladder (eg, MS)
tREAtmENt Pelvic floor muscle Kegel exercises, bladder Catheterization, relieve
strengthening (Kegel) training (timed voiding, obstruction (eg, α-blockers
exercises, weight loss, distraction or relaxation for BPH)
pessaries techniques), antimuscarinics
(eg, oxybutynin for overactive
bladder), mirabegron
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 599 11/7/19 5:42 PM