Page 712 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 712
668 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY
Pulmonary circulation Normally a low-resistance, high-compliance A consequence of pulmonary hypertension is cor
system. A in Pao causes a hypoxic pulmonale and subsequent right ventricular
2
vasoconstriction that shifts blood away from failure.
poorly ventilated regions of lung to well- Diffusion: V gas = A × D × P – P 2 where
˙
1
ventilated regions of lung. k Δ x
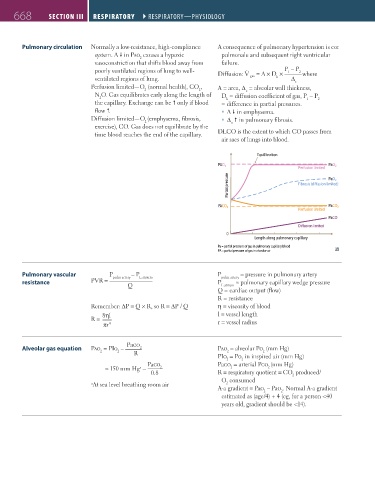
Perfusion limited—O (normal health), CO , A = area, Δ = alveolar wall thickness,
2
2
x
N O. Gas equilibrates early along the length of D = diffusion coefficient of gas, P – P
2
k
the capillary. Exchange can be only if blood = difference in partial pressures. 1 2
flow . A in emphysema.
Diffusion limited—O (emphysema, fibrosis, Δ in pulmonary fibrosis.
2
exercise), CO. Gas does not equilibrate by the x
time blood reaches the end of the capillary. DLCO is the extent to which CO passes from
air sacs of lungs into blood.
Equilibration
PAO₂ PaO₂
Perfusion limited
Partial pressure Fibrosis (di usion limited)
PaO₂
PACO₂ PaCO₂
Perfusion limited
PaCO
Di usion limited
0
Length along pulmonary capillary
Pa = partial pressure of gas in pulmonary capillary blood
PA = partial pressure of gas in alveolar air
Pulmonary vascular P pulm artery – P L atrium P pulm artery = pressure in pulmonary artery
resistance PVR = P L atrium ≈ pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Q
Q = cardiac output (flow)
R = resistance
Remember: ΔP = Q × R, so R = ΔP / Q η = viscosity of blood
8ηl l = vessel length
R = πr 4 r = vessel radius
Paco
Alveolar gas equation Pao = PIo – 2 Pao = alveolar Po (mm Hg)
2
2
R 2 2
PIo = Po in inspired air (mm Hg)
2
2
Paco Paco = arterial Pco (mm Hg)
a
≈ 150 mm Hg – 2 2 2
0.8 R = respiratory quotient = CO produced/
2
O consumed
a At sea level breathing room air 2
A-a gradient = Pao – Pao . Normal A-a gradient
2
2
estimated as (age/4) + 4 (eg, for a person <40
years old, gradient should be <14).
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 668 11/8/19 7:34 AM