Page 711 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 711
RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY seCtioN iii 667
Cyanide vs carbon Both inhibit aerobic metabolism via inhibition of complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) hypoxia
monoxide poisoning that does not fully correct with supplemental O and anaerobic metabolism.
2
Both can lead to pink or cherry red skin (usually postmortem finding), seizures, and coma.
Cyanide Carbon monoxide
SOURCE Byproduct of synthetic product combustion, Odorless gas from fires, car exhaust, or gas
ingestion of amygdalin (cyanogenic glucoside heaters.
found in apricot seeds) or cyanide.
TREATmENT Hydroxocobalamin (binds cyanide 100% O , hyperbaric O .
2 2
cyanocobalamin renal excretion).
Nitrites (oxidize Hb methemoglobin binds
cyanide cyanomethemoglobin less
toxicity).
Sodium thiosulfate ( cyanide conversion to
thiocyanate renal excretion).
SIgNS/SYmPTOmS Breath has bitter almond odor; cardiovascular Headache, dizziness.
A collapse. Multiple individuals may be involved (eg, family
with similar symptoms in winter).
Classically associated with bilateral globus
pallidus lesions on MRI A , although rarely
seen with cyanide toxicity as well.
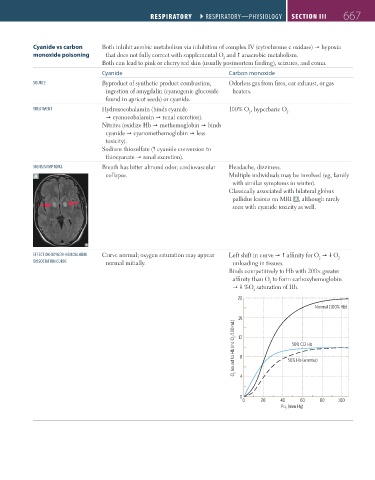
EFFECT ON OXYgEN-hEmOglObIN Curve normal; oxygen saturation may appear Left shift in curve affinity for O O
DISSOCIATION CURVE normal initially. unloading in tissues. 2 2
Binds competitively to Hb with 200× greater
affinity than O to form carboxyhemoglobin
2
%O saturation of Hb.
2
20
Normal (100% Hb)
O 2 bound to Hb (mL O 2 /100 mL) 16 8 50% Hb (anemia)
12
50% CO Hb
0 4
0 20 40 60 80 100
PO (mm Hg)
2
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 667 11/8/19 7:34 AM