Page 718 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 718
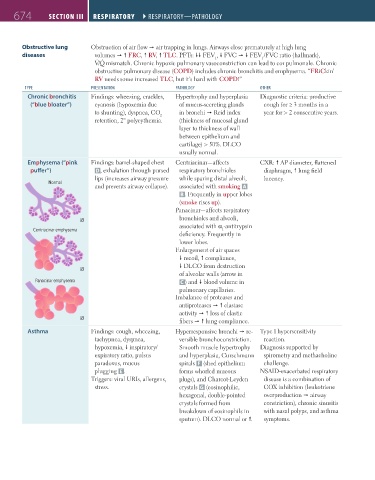
674 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY
Obstructive lung Obstruction of air flow air trapping in lungs. Airways close prematurely at high lung
diseases volumes FRC, RV, TLC. PFTs: FEV , FVC FEV /FVC ratio (hallmark),
1
1
˙ ˙
V/Q mismatch. Chronic hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction can lead to cor pulmonale. Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. “FRiCkin’
RV needs some increased TLC, but it’s hard with COPD!”
TYPE PRESENTATION PAThOlOgY OThER
Chronic bronchitis Findings: wheezing, crackles, Hypertrophy and hyperplasia Diagnostic criteria: productive
(“blue bloater”) cyanosis (hypoxemia due of mucus-secreting glands cough for ≥ 3 months in a
to shunting), dyspnea, CO in bronchi Reid index year for > 2 consecutive years.
2
retention, 2° polycythemia. (thickness of mucosal gland
layer to thickness of wall
between epithelium and
cartilage) > 50%. DLCO
usually normal.
Emphysema (“pink Findings: barrel-shaped chest Centriacinar—affects CXR: AP diameter, flattened
puffer”) D, exhalation through pursed respiratory bronchioles diaphragm, lung field
lips (increases airway pressure while sparing distal alveoli, lucency.
Normal
and prevents airway collapse). associated with smoking A
B . Frequently in upper lobes
(smoke rises up).
Panacinar—affects respiratory
bronchioles and alveoli,
associated with α -antitrypsin
Centriacinar emphysema 1
deficiency. Frequently in
lower lobes.
Enlargement of air spaces
recoil, compliance,
DLCO from destruction
of alveolar walls (arrow in
Panacinar emphysema C ) and blood volume in
pulmonary capillaries.
Imbalance of proteases and
antiproteases elastase
activity loss of elastic
fibers lung compliance.
Asthma Findings: cough, wheezing, Hyperresponsive bronchi re- Type I hypersensitivity
tachypnea, dyspnea, vers ible bronchoconstriction. reaction.
hypoxemia, inspiratory/ Smooth muscle hypertrophy Diagnosis supported by
expiratory ratio, pulsus and hyperplasia, Curschmann spirometry and methacholine
paradoxus, mucus spirals F (shed epithelium challenge.
plugging E . forms whorled mucous NSAID-exacerbated respiratory
Triggers: viral URIs, allergens, plugs), and Charcot-Leyden disease is a combination of
stress. crystals G (eosinophilic, COX inhibition (leukotriene
hexagonal, double-pointed overproduction airway
crystals formed from constriction), chronic sinusitis
breakdown of eosinophils in with nasal polyps, and asthma
sputum). DLCO normal or . symptoms.
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 674 11/8/19 7:34 AM