Page 720 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 720
676 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY
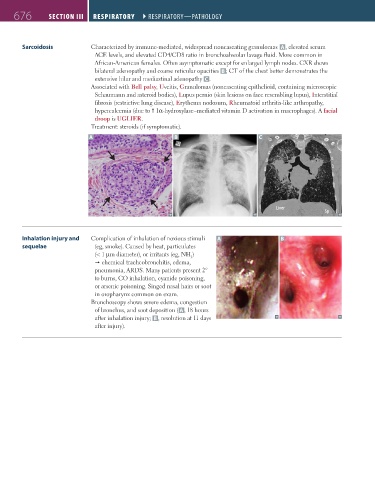
Sarcoidosis Characterized by immune-mediated, widespread noncaseating granulomas A , elevated serum
ACE levels, and elevated CD4/CD8 ratio in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. More common in
African-American females. Often asymptomatic except for enlarged lymph nodes. CXR shows
bilateral adenopathy and coarse reticular opacities B ; CT of the chest better demonstrates the
extensive hilar and mediastinal adenopathy C .
Associated with Bell palsy, Uveitis, Granulomas (noncaseating epithelioid, containing microscopic
Schaumann and asteroid bodies), Lupus pernio (skin lesions on face resembling lupus), Interstitial
fibrosis (restrictive lung disease), Erythema nodosum, Rheumatoid arthritis-like arthropathy,
hypercalcemia (due to 1α-hydroxylase–mediated vitamin D activation in macrophages). A facial
droop is UGLIER.
Treatment: steroids (if symptomatic).
A B C
Liver
Sp
Inhalation injury and Complication of inhalation of noxious stimuli A B
sequelae (eg, smoke). Caused by heat, particulates
(< 1 µm diameter), or irritants (eg, NH )
3
chemical tracheobronchitis, edema,
pneumonia, ARDS. Many patients present 2°
to burns, CO inhalation, cyanide poisoning,
or arsenic poisoning. Singed nasal hairs or soot
in oropharynx common on exam.
Bronchoscopy shows severe edema, congestion
of bronchus, and soot deposition ( A , 18 hours
after inhalation injury; B , resolution at 11 days
after injury).
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 676 11/8/19 7:34 AM