Page 719 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 719
RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY seCtioN iii 675
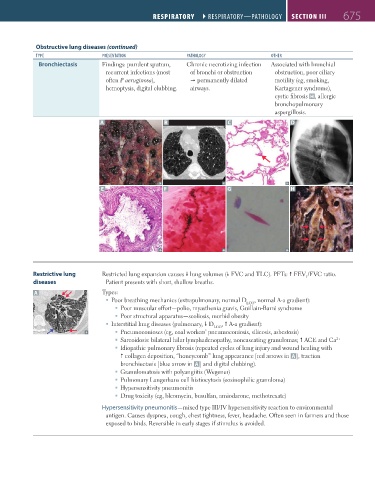
Obstructive lung diseases (continued)
TYPE PRESENTATION PAThOlOgY OThER
Bronchiectasis Findings: purulent sputum, Chronic necrotizing infection Associated with bronchial
recurrent infections (most of bronchi or obstruction obstruction, poor ciliary
often P aeruginosa), permanently dilated motility (eg, smoking,
hemoptysis, digital clubbing. airways. Kartagener syndrome),
cystic fibrosis H, allergic
bronchopulmonary
aspergillosis.
A B C D
E F G H
Restrictive lung Restricted lung expansion causes lung volumes ( FVC and TLC). PFTs: FEV /FVC ratio.
1
diseases Patient presents with short, shallow breaths.
A Types:
Poor breathing mechanics (extrapulmonary, normal D LCO , normal A-a gradient):
Poor muscular effort—polio, myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome
Poor structural apparatus—scoliosis, morbid obesity
Interstitial lung diseases (pulmonary, D LCO , A-a gradient):
Pneumoconioses (eg, coal workers’ pneumoconiosis, silicosis, asbestosis)
Sarcoidosis: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, noncaseating granulomas; ACE and Ca 2+
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (repeated cycles of lung injury and wound healing with
collagen deposition, “honeycomb” lung appearance [red arrows in A ], traction
bronchiectasis [blue arrow in A ] and digital clubbing).
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener)
Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis (eosinophilic granuloma)
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Drug toxicity (eg, bleomycin, busulfan, amiodarone, methotrexate)
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis—mixed type III/IV hypersensitivity reaction to environmental
antigen. Causes dyspnea, cough, chest tightness, fever, headache. Often seen in farmers and those
exposed to birds. Reversible in early stages if stimulus is avoided.
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 675 11/8/19 7:34 AM