Page 94 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 94
50 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR
Collagen Most abundant protein in the human body. Be So Totally Cool, Read Books.
Extensively modified by posttranslational
modification.
Organizes and strengthens extracellular matrix.
Type I Most common (90%)—Bone (made by Type I: bone.
osteoblasts), Skin, Tendon, dentin, fascia, production in osteogenesis imperfecta type I.
cornea, late wound repair.
Type II Cartilage (including hyaline), vitreous body, Type II: cartwolage.
nucleus pulposus.
Type III Reticulin—skin, blood vessels, uterus, fetal Type III: deficient in the uncommon, vascular
tissue, early wound repair. type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (ThreE D).
Type IV Basement membrane (basal lamina), lens. Type IV: under the floor (basement membrane).
Defective in Alport syndrome; targeted by
autoantibodies in Goodpasture syndrome.
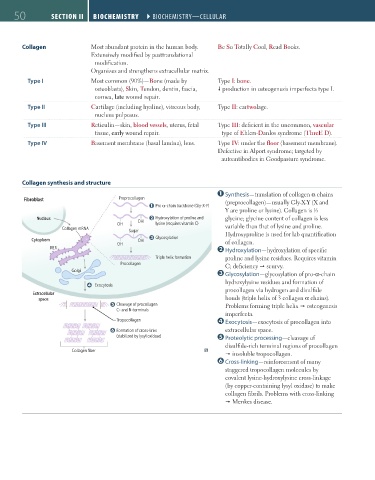
Collagen synthesis and structure
Synthesis—translation of collagen α chains
Fibroblast Preprocollagen (preprocollagen)—usually Gly-X-Y (X and
Pro α-chain backbone (Gly-X-Y)
Y are proline or lysine). Collagen is ⁄3
1
Nucleus OH Hydroxylation of proline and glycine; glycine content of collagen is less
OH lysine (requires vitamin C) variable than that of lysine and proline.
Collagen mRNA Sugar
Glycosylation Hydroxyproline is used for lab quantification
Cytoplasm OH of collagen.
OH
RER
Hydroxylation—hydroxylation of specific
Triple helix formation proline and lysine residues. Requires vitamin
Procollagen C; deficiency scurvy.
Golgi
Glycosylation—glycosylation of pro-α-chain
hydroxylysine residues and formation of
Exocytosis
procollagen via hydrogen and disulfide
Extracellular
space bonds (triple helix of 3 collagen α chains).
Cleavage of procollagen Problems forming triple helix osteogenesis
C- and N-terminals
imperfecta.
Tropocollagen Exocytosis—exocytosis of procollagen into
Formation of cross-links extracellular space.
(stabilized by lysyl oxidase) Proteolytic processing—cleavage of
disulfide-rich terminal regions of procollagen
Collagen fiber
insoluble tropocollagen.
Cross-linking—reinforcement of many
staggered tropocollagen molecules by
covalent lysine-hydroxylysine cross-linkage
(by copper-containing lysyl oxidase) to make
collagen fibrils. Problems with cross-linking
Menkes disease.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 50 11/7/19 3:16 PM