Page 96 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 96
52 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES
Elastin Stretchy protein within skin, lungs, large arteries, elastic ligaments, vocal cords, ligamenta flava
(connect vertebrae relaxed and stretched conformations).
Rich in nonhydroxylated proline, glycine, and lysine residues, vs the hydroxylated residues of
collagen.
Single Tropoelastin with fibrillin scaffolding.
elastin Stretch Cross-linking takes place extracellularly and gives elastin its elastic properties.
molecule Relax Cross-link
Broken down by elastase, which is normally inhibited by α 1 -antitrypsin.
α 1 -Antitrypsin deficiency results in unopposed elastase activity, which can cause COPD.
Changes with aging: dermal collagen and elastin, synthesis of collagen fibrils; cross-linking
remains normal.
A Marfan syndrome—autosomal dominant (with variable expression) connective tissue disorder
affecting skeleton, heart, and eyes. FBN1 gene mutation on chromosome 15 (fifteen) results in
defective fibrillin, a glycoprotein that forms a sheath around elastin. Findings: tall with long
extremities; pectus carinatum (more specific) or pectus excavatum A ; hypermobile joints; long,
tapering fingers and toes (arachnodactyly); cystic medial necrosis of aorta; aortic root aneurysm
rupture or dissection (most common cause of death); mitral valve prolapse. Subluxation of lenses,
typically upward and temporally (vs downward and medially in homocystinuria).
` `BIOCHEMISTRY—lABORATORY TECHNIqUES
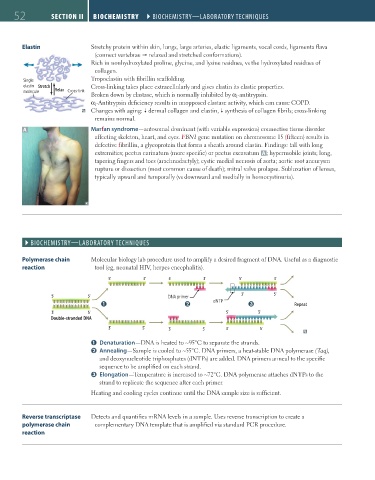
Polymerase chain Molecular biology lab procedure used to amplify a desired fragment of DNA. Useful as a diagnostic
reaction tool (eg, neonatal HIV, herpes encephalitis).
5' 3' 5' 3' 5' 3'
5' 3' DNA primer 3' 5'
dNTP
Repeat
3' 5' 5' 3'
Double-stranded DNA
3' 5' 3' 5' 3' 5'
Denaturation—DNA is heated to ~95°C to separate the strands.
Annealing—Sample is cooled to ~55°C. DNA primers, a heat-stable DNA polymerase (Taq),
and deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) are added. DNA primers anneal to the specific
sequence to be amplified on each strand.
Elongation—Temperature is increased to ~72°C. DNA polymerase attaches dNTPs to the
strand to replicate the sequence after each primer.
Heating and cooling cycles continue until the DNA sample size is sufficient.
Reverse transcriptase Detects and quantifies mRNA levels in a sample. Uses reverse transcription to create a
polymerase chain complementary DNA template that is amplified via standard PCR procedure.
reaction
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 52 11/7/19 3:16 PM