Page 478 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 478
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
Fresh Fresh
air inlet air inlet Fan
Flue
gases
outlet
Fresh
air inlet
Flue
gases
outlet
Gas burner
Gas burner
Room sealed
boiler casing
Room sealed
boiler casing
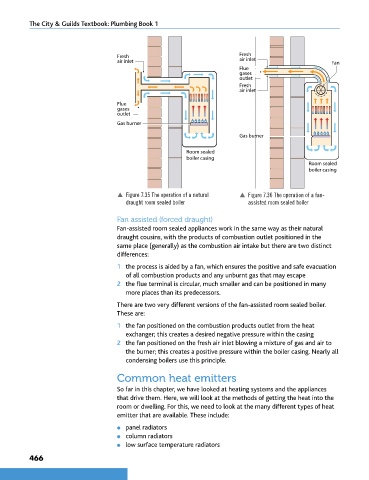
p Figure 7.35 The operation of a natural p Figure 7.36 The operation of a fan-
draught room sealed boiler assisted room sealed boiler
Fan assisted (forced draught)
Fan-assisted room sealed appliances work in the same way as their natural
draught cousins, with the products of combustion outlet positioned in the
same place (generally) as the combustion air intake but there are two distinct
differences:
1 the process is aided by a fan, which ensures the positive and safe evacuation
of all combustion products and any unburnt gas that may escape
2 the flue terminal is circular, much smaller and can be positioned in many
more places than its predecessors.
There are two very different versions of the fan-assisted room sealed boiler.
These are:
1 the fan positioned on the combustion products outlet from the heat
exchanger; this creates a desired negative pressure within the casing
2 the fan positioned on the fresh air inlet blowing a mixture of gas and air to
the burner; this creates a positive pressure within the boiler casing. Nearly all
condensing boilers use this principle.
Common heat emitters
So far in this chapter, we have looked at heating systems and the appliances
that drive them. Here, we will look at the methods of getting the heat into the
room or dwelling. For this, we need to look at the many different types of heat
emitter that are available. These include:
l panel radiators
l column radiators
l low surface temperature radiators
466
9781510416482.indb 466 29/03/19 9:03 PM