Page 359 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 359
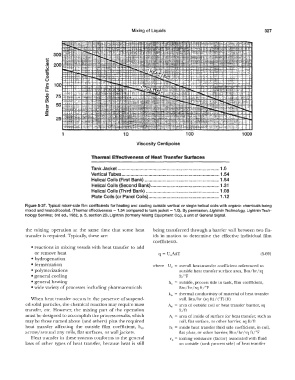
Mixing of Liquids 327
1 10 100 1000
Viscosity Centipoise
Thermal Effectiveness of Heat Transfer Surfaces
Tank Jacket 1.0
Vertical Tubes 1.54
Helical Coils (First Bank) 1.54
Helical Coils (Second Bank) 1.31
Helical Coils {Third Bank) 1.08
Plate Coils (or Panel Coils) , .12
Figure 5-37. Typical mixer-side film coefficients for heating and cooling outside vertical or single helical coils with organic chemicals being
mixed and heated/cooled. (Thermal effectiveness = 1.54 compared to tank jacket = 1.0). By permission, Lightnin Technology, Lightnin Tech-
nology Seminar, 3rd ed., 1982, p. 5, section 20, Lightnin (formerly Mixing Equipment Co.), a unit of General Signal.
the m1xmg operation at the same time that some heat being transferred through a barrier wall between two flu-
transfer is required. Typically, these are: ids in motion to determine the effective individual film
coefficients.
• reactions in mixing vessels with heat transfer to add
or remove heal q=Uc,MT (5-69)
• hydrogenation
• fermentation where U 0 = overall heat-transfer coefficient referenced to
• polymerizations outside heat transfer surface area, Btu/hr I sq
• general cooling ft/°F
• general heating h., = outside, process side in tank, film coefficient,
• wide variety of processes including pharmaceuticals Btu/hr /sq ft/°F
kw = thermal conductivity of material of heat transfer
When heat transfer occurs in the presence of suspend- wall, Btu/hr (sq ft) I (°F) (ft)
ed solid particles, the chemical reaction may require mass A., = area of outside coil or heat transfer barrier, sq
transfer, etc. However, the mixing part of the operation ft/ft
must be designed to accomplish the process results, which A; = area of inside of surface for heat transfer, such as
may be those named above (and others) plus the required coil, flat surface, or other barrier, sq ft/ft
heat transfer affecting the outside film coefficient, h 0, hi = inside heat transfer fluid side coefficient, in coil,
across/ around any coils, flat surfaces, or wall jackets. flat plate, or other barrier, Btu/hr/sq ft/°F
Heat transfer in these systems conforms to the general r0 = fouling resistance (factor) associated with fluid
laws of other types of heat transfer, because heat is still on outside (tank process side) of heat transfer