Page 473 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 473
Process Safety and Pressure-Relieving Devices 439
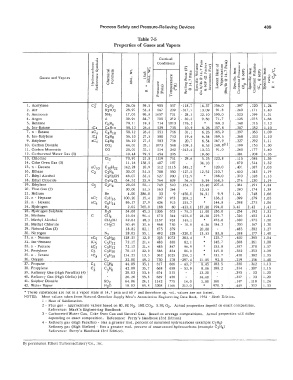
Table 7-5
Properties of Gases and Vapors
Critical
Conditions
Gases and Vapors
1. Acetylene C2 C2H2 26.04 59.5 905 557 -118.7 14.37 356.0 .397 .320 1.24
2. Air Nz+02 28.97 53.3 547 239 -317.7 13.09 91.8 .240 .171 1.40
3. Ammonia NH3 17.03 90.8 1657 731 - 28.l 22.10 590.0 .523 .399 1.31
4. Argon A 39.94 38.7 705 272 - 30.3 9.50 71.7 .125 .075 1.66
5. Benzene C6H6 78.11 19.8 714 1013 176.2 • 169.3 .240 .215 1.12
_6�.-'- l s�o_-�Bu�t_a_ne.:...._ -+-= i C4 C4H10_-+-_5_8_._1_ 2 -+-_2_6_._6--+-_5_29_,__7_3_5--+ __ l_0_ . 9--+- __ 6_._2_6--+-_ 1 5_7_._8_--+-_ . _ 3 8_7_-+-'-3_5_2___,_l_._l_O�
7.n-Butane nC � -·-c\H10 58.12 26.6 551 766 31.1 6.25 165.9 .397 .363 1.09
8. Iso-Butylene iC4 C4H8 56.10 27.5 580 753 19.6 6.54 169.5 .368 .333 1.10
9. Butylene nC4 C4H8 56.10 27. s '!i83 756 20. 7 6. 54 167. 9 . 327 . 292 1.11
10. Carbon Dioxide C02 44.01 35.l 1073 548 -109.3 8.53 248.8(1) I .199 .153 1.30
11. Carbon Monoxide CO 28.01 55.1 514 242 -313.6 13.55 91.0 , .246 .177 1.40
12. CarburetedWaterGas(3) - 19.48 79.5 454 235 - 19.60 - .281 .208 1.35
13. Chlorine Cl2 70.91 21.8 lll9 751 - 29.6 5. 25 123.8 . il5 .08,1 1.36
14. Coke0venGas(3) - 11.16 138.5 407 197 - 34.10 - .679 .514 1.32
15, n - Decane nC10 C10H22 142.28 10.9 312 1115 345.2 • 120.0 .401 .387 1.03
16. Ethane c2 C2H6 30.07 51.5 708 550 -127.5 12.52 210.7 .410 .343 1.19
17. Ethyl Alcohol C2H50H 46.07 33.5 927 930 172.9 • 368.0 .370 .328 1.13
_ 1 8_._E_ t h � y-l_c_ · h_w_r_i_d_ e --+---+-C_zH4C_ l -+-_64_._5_2-+_2_3_ . 9___,_7_6_4--+_8_2_ 9 -+-_5_4 � ._4-+-- � 5 � . 5 � 9___,_1_6_8 � . 5'---+--'" � 2-7 � 4--jf-'- ' � 2 3 � 0'--+..:cl � . � 1 9'---
19. Ethylene C 2 C2H4 28.05 55,1 749 510 -154.7 13.40 207.6 .361 .291 1.24
20. Flue Gas (2) - 30.00 51.5 563 264 - 12.63 - .240 .174 1.38
21. Helium He 4.00 386.0 33 9 -450.0 94.91 9.9 1.24 . 748 1.66
22. n - Heptane nC7 C7H16 100.20 15.4 397 973 209.2 • 136.2 .399 .379 I.OS
23. n - Hexane nC6 C6H14 86.17 17.9 434 915 155.7 • 144,8 .398 .375 , I.06
7
7
7
_2 � 4 � ·-Hy=-:-d � r_o � g_e_n-=-.,.....,....,....,. � ------+----+-:-cH2=----+---=- 2 ._0 � 2-+_7_6 5_ . 0::-t--:-c1 � 8 � 8-+--,=60-:--t- - 4-2 � 3-. 0-+--1-8_7_ . 8 � 0::-t-1 � 9 � 4- . 0,---+-3-._4 � 1--+-2- . 4-2,---+ ) -1_ . 4_1 __
25. Hydrogen Sulphide H2S 34.08 45.3 1306 673 - 76.5 11.00 236.0 I .254 .192 1.32
26. Methane C CH4 16.04 96.4 673 344 -258.8 23.50 219.7 I .526 .402 1.31
27.Methy!Alcohol I CH30H 32.04 48.3 1157 924 148.l • 473.0 .330 .275 1.20
28. Methyl Chloride CH3Cl 50. 49 30. 6 968 750 - 10. 8 6. 26 184. 2 . 200 . 167 1. 20
29.Natura!Gas(3) I - 18.82 82.1 675 379 - 20.00 - .485 .382 1.27
_3 � 0-._N_ i t-ro � g � e_n +---=-+--Nz -+-_28_._0 � 2-+_5_5_ . 1::-t_4_9_2-+_2 � 28-:--1-- - 3-2_0_ . _0-+--l-3 � . 5-3--+-8 � 5 � . 8--+---''-2_4_8___,-'- . - 1 7_7_+- l � . 4-0 �
31. n - Nonane nC9 C9H20 128.25 12.0 3}5 1073 303.4 • 125. 7 .400 .385 1.04
32. Iso-Pentane IC5 C5H12 72.15 21.4 483 830 82.1 • 145.7 .388 .361 1.08
33. 11 - Pentane n<::s C5H12 72.15 21.4 485 847 96.9 • 153.8 .397 .370 1.07
34. Pentylene C5 C5H10 70.13 22.0 586 854 86.0 • 149.0 .382 .353 1.08
35.n-Octane nC8 C8H18 114.22 13.5 362 1025 258.2 • 131.7 .400 .382 1.05
-3 � 6_._o � xy � g � e_n -+--=---+-,02---+--32_._o � o-+_4=8_ . 3::-t_7_3 � 0-+-2 � 7 8-1-- - 2-9_7_ . _4+--l- l � . 8 � 5--+-9 � 2 � . o--+ , _._2 � i � 9--+'-'- " l-5_6_1-- l � . 4_0 �
37. Propane C3 C3H8 44.09 .35.1 617 666 43.7 8.45 183.5 .388 J .342 1.13
38. Propylene Cj C3H6 42.08 36.7 668 658 - 53.9 8.86 188.2 I .354 ! .307 1.15
39. RefineryGas(HighParaffin)(4) - 28.83 53.6 674 515 - 1 13.20 - .395 33 1.20
40. Refinery Gas (High Olefin)(4) - 26.26 58.8 639 456 - 14.40 - ! ' .397 33 l.20
41. Sulphur Dioxide S02 64.06 24.l 1142 775 14.0 5.80 168 .147 .118 1.24
42. Water Vapor H20 18.02 85.8 3208 1166 212.0 • 970.3 .445 .332 1.33
• These substances are not in a vapor state at 14. 7 psia and 60 F and therefore sp. vol. values are not listed,
NOTES: Most values taken from Natural Gasoline Supply Men's Association Engineering Data Book, 1951 - Sixth Edition.
l - Heat of Sublimation.
2 - Flue gas·· Approximate values based on 80.5% N2, 16% co2, 3.5% 02. Actual properties depend on exact composition.
Reference: Mark's Engineering Handbook
3 - Carbureted Water Gas, Coke Oven Gas and Natural Gas. Based on average compositions. Actual properties will differ
depending on exact composition. Reference: Perry's Handbook (3rd Edition)
4 - Refinery gas (High Paraffin) - Has a greater mol. percent of saturated hydrocarbons (example C2H6)
Refinery gas (High Olefins) - Has a greater mol. percent of unsaturated hydrocarbons (example C2H4)
Reference: Perry's Handbook (3rd Edition).
By permission Elliott Turbornachinery Co., Inc.