Page 533 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 533
Applied Process Design 499
Table 7-25A Table 7-25B
Selected Over-pressure Failure Situations Physiological Effects of Blast Over-pressures
Avg Over- Physiological Effects Peak Over-
Damage Limits: pressure (PSI) of Blast Pressures pressure (PSI)
Crater 280 Knock Personnel Down 1
Probable Total Destruction 10 & Above { Threshold 5
Limit Serious Structural Damage 2.3 Eardrum Rupture 50% 15
Limit Earth Wave Damage 1.2 { Threshold 30-40
Limit Minor Structural Damage 0.4 Lung Damage Severe 80 & up
Missile Limit 0.3 l !hreshold 100-120
Typical Glass Failure 0.15 Lethality :>0% 130-180
Limit Glass Breakage 0.006 Near 100% 200-250
By permission, Stull [41] Dow Chemical Co. and American Institute of By permission, Stull [41] Dow Chemical Co. and American Institute of
Chemical Engineers, Monograph Series, No. 10, V. 73 (1977). Chemical Engineers, Monograph. Series, No. 10, V. 73 (1977).
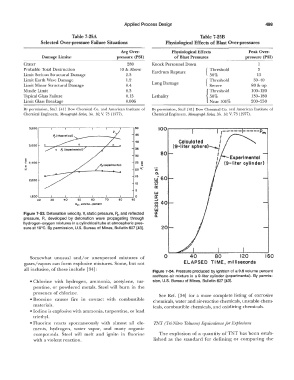
100.--��-,.�������...-�--,,,.....-,
,----- ----Pm
45 I
40 Calculated I
3,000 (9-liter sphere)--{
35
80 I
.. 30 I
u
� 2,500 Ps (experimental) 25 !. I
0
E
::: 20 �- II)
a.
15
2,000 u.i 60
10 !!?
a::
5
LU
1,500L----'--�----'---�--..._ __ ..__ _ __, 0 er
ro � � � ro ro � �
Hz 1 volume- percent � 40
(/)
I.LI
Figure 7-53. Detonation velocity, V, static pressure, P,,, and reflected tr
a.
pressure, P,., developed by detonation wave propagating through
hydrogen-oxygen mixtures in a cylindrical tube at atmospheric pres-
sure at 18°C. By permission, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Bulletin 627 [43]. 20
Somewhat unusual and/ or unexpected mixtures of 0 40 80 120 160
gases/vapors can form explosive mixtures. Some, but not ELAPSED TIME, milliseconds
all inclusive, of these include [34]: Figure 7-54. Pressure produced by ignition of a 9.6 volume percent
methane-air mixture in a 9-liter cylinder (experimental). By permis-
• Chlorine with hydrogen, ammonia, acetylene, tur- sion, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Bulletin 627 [43].
pentine, or powdered metals. Steel will burn in the
presence of chlorine. See Ref. [34] for a more complete listing of corrosive
• Bromine causes fire in contact with combustible chemicals, water and air-reactive chemicals, unstable chem-
materials. icals, combustible chemicals, and oxidizing chemicals.
• Iodine is explosive with ammonia, turpentine, or lead
triethyl,
• Fluorine reacts spontaneously with almost all ele- TNT (Tri-Nitro Toluene) Equivalence for Explosions
ments, hydrogen, water vapor, and many organic
compounds. Steel will melt and ignite in fluorine The explosion of a quantity of TNT has been estab-
with a violent reaction. lished as the standard for defining or comparing the