Page 12 - Computing book 6
P. 12
Analysing Data Class 6
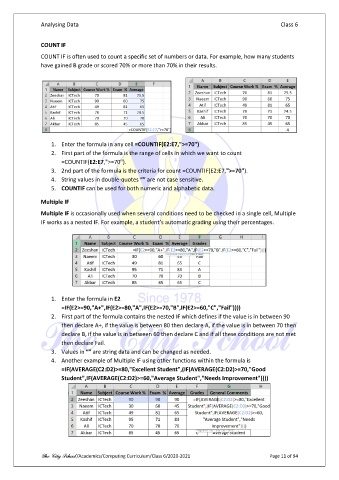
COUNT IF
COUNT IF is often used to count a specific set of numbers or data. For example, how many students
have gained B grade or scored 70% or more than 70% in their results.
1. Enter the formula in any cell =COUNTIF(E2:E7,">=70")
2. First part of the formula is the range of cells in which we want to count
=COUNTIF(E2:E7,">=70").
3. 2nd part of the formula is the criteria for count =COUNTIF(E2:E7,">=70").
4. String values in double-quotes “” are not case sensitive.
5. COUNTIF can be used for both numeric and alphabetic data.
Multiple IF
Multiple IF is occasionally used when several conditions need to be checked in a single cell, Multiple
IF works as a nested IF. For example, a student’s automatic grading using their percentages.
1. Enter the formula in E2
=IF(E2>=90,"A+",IF(E2>=80,"A",IF(E2>=70,"B",IF(E2>=60,"C","Fail"))))
2. First part of the formula contains the nested IF which defines if the value is in between 90
then declare A+, if the value is between 80 then declare A, if the value is in between 70 then
declare B, if the value is in between 60 then declare C and if all these conditions are not met
then declare Fail.
3. Values in “” are string data and can be changed as needed.
4. Another example of Multiple IF using other functions within the formula is
=IF(AVERAGE(C2:D2)>=80,"Excellent Student",(IF(AVERAGE(C2:D2)>=70,"Good
Student",IF(AVERAGE(C2:D2)>=60,"Average Student","Needs Improvement"))))
The City School /Academics/Computing Curriculum/Class 6/2020-2021 Page 11 of 94