Page 115 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 115
(c) For the 4 W and 12 W resistors: CHAPTER 3
Potential difference, V = V + V 2 So, the current flowing While the current flowing Electricity
1
V = V – V through the 4 W resistor, through the 12 W resistor,
2 1
= 6 – 2.4 V 2 V 3
= 3.6 V I = R I = R
2
3
2 3
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
Since R is parallel with R , = 3.6 = 3.6
2
3
Then, V = V = 3.6 V 4 12
3 2 = 0.9 A = 0.3 A
Example 2
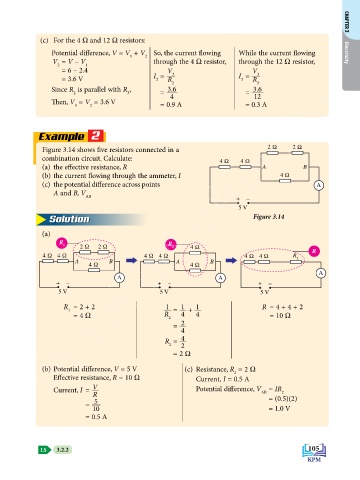
Figure 3.14 shows five resistors connected in a 2 Ω 2 Ω
combination circuit. Calculate: 4 Ω 4 Ω
(a) the effective resistance, R A B
(b) the current flowing through the ammeter, I 4 Ω
(c) the potential difference across points A
A and B, V
AB
+ –
5 V
Solution Figure 3.14
(a)
R
1 R
2 Ω 2 Ω 2 4 Ω
R
4 Ω 4 Ω 4 Ω 4 Ω 4 Ω 4 Ω R 2
A B A B
4 Ω 4 Ω
A
A A
+ – + – + –
5 V 5 V 5 V
1
R = 2 + 2 1 = + 1 R = 4 + 4 + 2
1
= 4 W R 2 4 4 = 10 W
= 2
4
R = 4
2 2
= 2 W
(b) Potential difference, V = 5 V (c) Resistance, R = 2 W
2
Effective resistance, R = 10 W Current, I = 0.5 A
Current, I = V Potential difference, V = IR
2
R AB = (0.5)(2)
= 5
10 = 1.0 V
= 0.5 A
3.2.2
LS 3.2.2 105