Page 410 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 410
280 PART 3: Cardiovascular Disorders
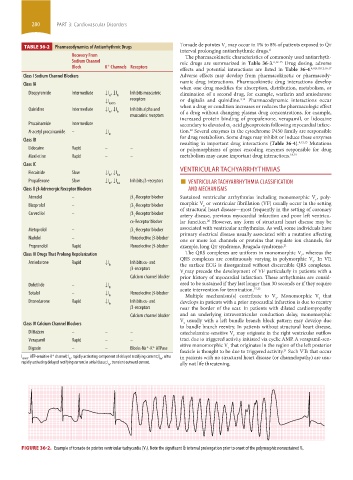
Torsade de pointes V may occur in 1% to 8% of patients exposed to Q ˙ t
TABLE 36-2 Pharmacodynamics of Antiarrhythmic Drugs t
interval prolonging antiarrhythmic drugs. 4
Recovery From The pharmacokinetic characteristics of commonly used antiarrhyth-
Sodium Channel mic drugs are summarized in Table 36-3. 6,12-15 Drug dosing, adverse
Block K Channels Receptors effects and potential interactions are listed in Table 36-4. 4,6,8,10,12,16,17
+
Class I Sodium Channel Blockers Adverse effects may develop from pharmacokinetic or pharmacody-
namic drug interactions. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions develop
Class IA
when one drug modifies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, or
Disopyramide Intermediate ↓I , ↓I Inhibits muscarinic elimination of a second drug, for example, warfarin and amiodarone
to Kr
4,12
↓I receptors or digitalis and quinidine. Pharmacodynamic interactions occur
K(ATP) when a drug or condition increases or reduces the pharmacologic effect
Quinidine Intermediate ↓I , ↓I Inhibits alpha and
to Kr of a drug without changing plasma drug concentrations, for example,
muscarinic receptors
increased protein binding of propafenone, verapamil, or lidocaine
Procainamide Intermediate secondary to elevated α -acid glycoprotein following myocardial infarc-
1
12
N-acetyl procainamide – ↓I tion. Several enzymes in the cytochrome P450 family are responsible
Kr for drug metabolism. Some drugs may inhibit or induce these enzymes
Class IB
resulting in important drug interactions (Table 36-4). 4,12,13 Mutations
Lidocaine Rapid – – or polymorphisms of genes encoding enzymes responsible for drug
Mexiletine Rapid – – metabolism may cause important drug interactions. 18,19
Class IC
Flecainide Slow ↓I , ↓I VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
Kr Kur
Propafenone Slow ↓I , ↓I Inhibits β-receptors ■ VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA CLASSIFICATION
Kr Kur
Class II β-Adrenergic Receptor Blockers AND MECHANISMS
Atenolol – β -Receptor blocker Sustained ventricular arrhythmias including monomorphic V , poly-
1 t
Bisoprolol – β -Receptor blocker morphic V or ventricular fibrillation (VF) usually occur in the setting
t
1 of structural heart disease—most frequently in the setting of coronary
Carvedilol – β -Receptor blocker
1 artery disease, previous myocardial infarction and poor left ventricu-
α-Receptor blocker lar function. However, any form of structural heart disease may be
20
Metoprolol – β -Receptor blocker associated with ventricular arrhythmias. As well, some individuals have
1 primary electrical disease usually associated with a mutation affecting
Nadolol – Nonselective β-blocker one or more ion channels or proteins that regulate ion channels, for
Propranolol Rapid Nonselective β-blocker example, long Q ˙ t syndrome, Brugada syndrome. 21
Class III Drugs That Prolong Repolarization The QRS complexes are uniform in monomorphic V , whereas the
t
QRS complexes are continuously varying in polymorphic V . In VF,
Amiodarone Rapid ↓I Inhibits α- and t
Kr the surface ECG is disorganized without discernible QRS complexes.
β-receptors
V may precede the development of VF particularly in patients with a
t
Calcium channel blocker prior history of myocardial infarction. These arrhythmias are consid-
Dofetilide – ↓I ered to be sustained if they last longer than 30 seconds or if they require
Kr acute intervention for termination. 15,22
Sotalol – ↓I Nonselective β-blocker
Kr Multiple mechanism(s) contribute to V . Monomorphic V that
t
t
Dronedarone Rapid ↓I Inhibits α- and develops in patients with a prior myocardial infarction is due to reentry
Kr
β-receptors near the border of the scar. In patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
Calcium channel blocker and an underlying intraventricular conduction delay, monomorphic
V usually with a left bundle branch block pattern may develop due
Class IV Calcium Channel Blockers t
to bundle branch reentry. In patients without structural heart disease,
Diltiazem – – – catecholamine-sensitive V may originate in the right ventricular outflow
t
Verapamil Rapid – – tract due to triggered activity initiated via cyclic AMP. A verapamil-sen-
sitive monomorphic V that originates in the region of the left posterior
+
Digoxin – – Blocks-Na -K ATPase t
+
fascicle is thought to be due to triggered activity. Such VTs that occur
21
+
I K(ATP) , ATP-sensitive K channel; I , rapidly activating component of delayed rectifying current; I , ultra in patients with no structural heart disease (or channelopathy) are usu-
Kr
Kur
rapidly activating delayed rectifying current in atrial tissue; I , transient outward current. ally not life threatening.
to
FIGURE 36-2. Example of torsade de pointes ventricular tachycardia (V T). Note the significant Qt interval prolongation prior to onset of the polymorphic nonsustained V t.
˙
section03.indd 280 1/23/2015 2:07:08 PM