Page 412 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 412
282 PART 3: Cardiovascular Disorders
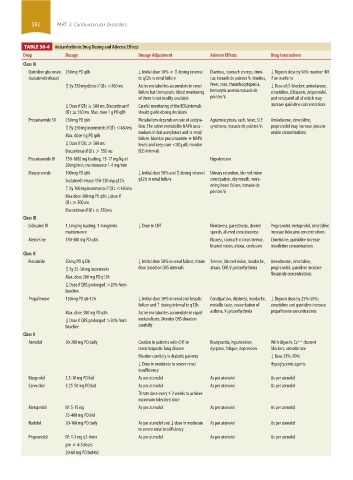
TABLE 36-4 Antiarrhythmic Drug Dosing and Adverse Effects
Drug Dosage Dosage Adjustment Adverse Effects Drug Interactions
Class IA
Quinidine gluconate 250 mg PO q8h ↓ Initial dose 50% + ↑ dosing interval Diarrhea, stomach cramps, tinni- ↓ Digoxin dose by 50% monitor INR
(sustained release) to q12h in renal failure tus; torsade de pointes V T tinnitus, if on warfarin
↑ By 250 mg doses if QTc <460 ms Active metabolites accumulate in renal fever, rash, thrombocytopenia, ↓ Dose of β-blocker; amiodarone,
failure but therapeutic blood monitoring hemolytic anemia torsade de cimetidine, diltiazem, propranolol,
of them is not readily available pointes V T and verapamil all of which may
↓ Dose if QTc ≥ 500 ms. Discontinue if Careful monitoring of the ECG intervals increase quinidine concentrations
QTc ≥ 550 ms. Max. dose 1 g PO q8h should guide dosing decisions
Procainamide SR 250 mg PO q6h Metabolism depends on rate of acetyla- Agranulocytosis, rash, fever, SLE Amiodarone, cimetidine,
↑ By 250 mg increments if QTc <460 ms tion. The active metabolite NAPA accu- syndrome, torsade de pointes V T propranolol may increase procain-
mulates in fast acetylators and in renal amide concentrations
Max. dose 1 g PO q6h failure. Monitor procainamide + NAPA
↓ Dose if QTc ≥ 500 ms. levels and keep sum <80 µM; monitor
Discontinue if QTc > 550 ms ECG intervals
Procainamide IV 750-1000 mg loading; 15-17 mg/kg at Hypotension
20 mg/min; maintenance 1-4 mg/min
Disopyramide 100 mg PO q8h ↓ Initial dose 50% and ↑ dosing interval Urinary retention, blurred vision
Sustained release 150-250 mg q12h q12h in renal failure constipation, dry mouth, wors-
ening heart failure, torsade de
↑ By 100 mg increments if QTc <460 ms
pointes V T
Max dose 300 mg PO q8h ↓dose if
QTc ≥ 500 ms
Discontinue if QTc ≥ 550 ms
Class IB
Lidocaine IV 1.5 mg/kg loading; 1-4 mg/min ↓ Dose in CHF Numbness, paresthesia, slurred Propranolol, metoprolol, cimetidine
maintenance speech, altered consciousness increase lidocaine concentrations
Mexiletine 150-300 mg PO q8h Nausea, stomach cramps tremor, Cimetidine, quinidine increase
blurred vision, ataxia, confusion mexiletine concentrations
Class IC
Flecainide 50 mg PO q12h ↓ Initial dose 50% in renal failure; titrate Tremor, blurred vision, headache, Amiodarone, cimetidine,
↑ By 25-50 mg increments dose based on QRS intervals ataxia, CHF,V T proarrhythmia propranolol, quinidine increase
flecainide concentrations
Max. dose 200 mg PO q12h
↓ Dose if QRS prolonged >20% from
baseline
Propafenone 150 mg PO q8-12h ↓ Initial dose 50% in renal and hepatic Constipation, dizziness, headache, ↓ Digoxin dose by 25%-50%;
failure and ↑ dosing interval to q12h metallic taste, exacerbation of cimetidine and quinidine increase
Max. dose 300 mg PO q8h Active metabolites accumulate in rapid asthma, V T proarrhythmia propafenone concentrations
↓ Dose if QRS prolonged >20% from metabolizers. Monitor QRS duration
baseline carefully
Class II
Atenolol 50-200 mg PO daily Caution in patients with CHF or Bradycardia, hypotension, With digoxin, Ca channel
++
bronchospastic lung disease dyspnea, fatigue, depression blockers, amiodarone
Monitor carefully in diabetic patients ↓ Dose 25%-50%
↓ Dose in moderate to severe renal Hypoglycemic agents
insufficiency
Bisoprolol 2.5-10 mg PO bid As per atenolol As per atenolol As per atenolol
Carvedilol 3.25-50 mg PO bid As per atenolol As per atenolol As per atenolol
Titrate dose every 1-2 weeks to achieve
maximum tolerated dose
Metoprolol IV: 5-15 mg As per atenolol As per atenolol As per atenolol
25-400 mg PO bid
Nadolol 20-160 mg PO daily As per atenolol and ↓ dose in moderate As per atenolol As per atenolol
to severe renal insufficiency
Propranolol IV: 1-2 mg q2-4min As per atenolol As per atenolol As per atenolol
prn × 4-5 doses
20-80 mg PO bid-tid
section03.indd 282 1/23/2015 2:07:09 PM