Page 413 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 413
CHAPTER 36: Cardiac Arrhythmias, Pacing, Cardioversion, and Defibrillation in the Critical Care Setting 283
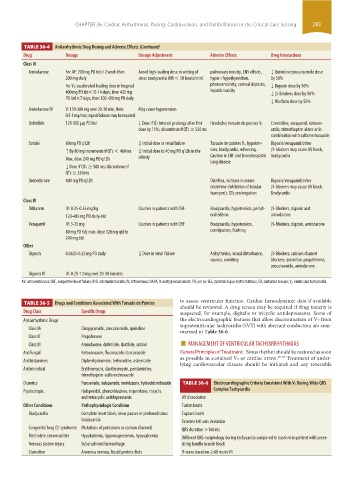
TABLE 36-4 Antiarrhythmic Drug Dosing and Adverse Effects (Continued)
Drug Dosage Dosage Adjustment Adverse Effects Drug Interactions
Class III
Amiodarone For AF: 200 mg PO tid×2 week then Avoid high loading dose in setting of pulmonary toxicity, CNS effects, ↓ Quinidine/procainamide dose
200 mg daily sinus bradycardia (HR < 50 beats/min) hyper-/hypothyroidism, by 50%
For V T: accelerated loading dose in hospital photosensitivity, corneal deposits, ↓ Digoxin dose by 50%
400 mg PO tid×10-14 days, then 400 mg hepatic toxicity ↓ β-Blockers dose by 50%
PO bid×7 days, then 300-400 mg PO daily
↓ Warfarin dose by 50%
Amiodarone IV V: 150-300 mg over 20-30 min, then May cause hypotension
0.5-1 mg/min; repeat boluses may be required
Dofetilide 125-500 µg PO bid ↓ Dose if Q ˙ t interval prolongs after first Headache; torsade de pointes V T Cimetidine, verapamil, ketocon-
dose by 15%; discontinue if QTc ≥ 550 ms azole, trimethoprim alone or in
combination with sulfamethoxazole
Sotalol 80 mg PO q12h ↓ Initial dose in renal failure Torsade de pointes V T, hypoten- Digoxin/verapamil/other
↑ By 80 mg increments if QTc < 460 ms ↓ Initial dose to 40 mg PO q12h in the sion, bradycardia, wheezing. β-blockers may cause AV block,
Max. dose 240 mg PO q12h elderly Caution in CHF and bronchospastic bradycardia
lung disease
↓ Dose if QTc ≥ 500 ms; discontinue if
QTc ≥ 550 ms
Dronedarone 400 mg PO q12h Diarrhea, increase in serum Digoxin/verapamil/other
creatinine (inhibition of tubular β-blockers may cause AV block.
transport), QTc prolongation Bradycardia
Class IV
Diltiazem IV: 0.25-0.35 mg/kg Caution in patients with CHF Bradycardia, hypotension, periph- β-Blockers, digoxin and
120-480 mg PO daily-bid eral edema amiodarone
Verapamil IV: 5-15 mg Caution in patients with CHF Bradycardia, hypotension, β-Blockers, digoxin, amiodarone
80 mg PO tid; max. dose 120 mg qid to constipation, flushing
240 mg bid
Other
Digoxin 0.0625-0.25 mg PO daily ↓ Dose in renal failure Arrhythmias, visual disturbance, β-Blockers; calcium channel
nausea, vomiting blockers, quinidine, propafenone,
procainamide, amiodarone
Digoxin IV IV: 0.25-1.0 mg over 20-30 minutes
AV, atrioventricular; CHF, congestive heart failure; INR, international ratio; IV, intravenous; NAPA, N-acetylprocainamide; PO, per os; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SR, sustained release; V , ventricular tachycardia.
T
TABLE 36-5 Drugs and Conditions Associated With Torsade de Pointes to assess ventricular function. Cardiac hemodynamic data if available
should be reviewed. A drug screen may be required if drug toxicity is
Drug Class Specific Drugs suspected, for example, digitalis or tricyclic antidepressants. Some of
Antiarrhythmic Drugs the electrocardiographic features that allow discrimination of V T from
supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) with aberrant conduction are sum-
Class IA Disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine
marized in Table 36-6.
Class IC Propafenone ■
Class III Amiodarone, dofetilide, ibutilide, sotalol MANAGEMENT OF VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
Antifungal Ketoconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole General Principles of Treatment: Sinus rhythm should be restored as soon
as possible in sustained V T or cardiac arrest. 25-27 Treatment of under-
Antihistamines Diphenhydramine, terfenadine, astemizole
lying cardiovascular disease should be initiated and any reversible
Antimicrobial Erythromycin, clarithromycin, pentamidine,
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Diuretics Furosemide, indapamide, metolazone, hydrochlorothiazide TABLE 36-6 Electrocardiographic Criteria Consistent With V T During Wide QRS
Psychotropic Haloperidol, phenothiazines, risperidone, tricyclic Complex Tachycardia
and tetracyclic antidepressants AV dissociation
Other Conditions Pathophysiologic Condition Fusion beats
Bradycardia Complete heart block, sinus pauses or profound sinus Capture beats
bradycardia Extreme left axis deviation
Congenital long Q t syndrome Mutations of potassium or sodium channels QRS duration >160 ms
˙
Electrolyte abnormalities Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia Different QRS morphology during tachycardia compared to baseline in patient with preex-
Nervous system injury Subarachnoid hemorrhage isting bundle branch block
Starvation Anorexia nervosa, liquid protein diets R-wave duration ≥60 ms in V1
section03.indd 283 1/23/2015 2:07:10 PM