Page 188 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 188
ECA3 7/18/06 6:45 PM Page 173
The bones and joints of the upper limb 173
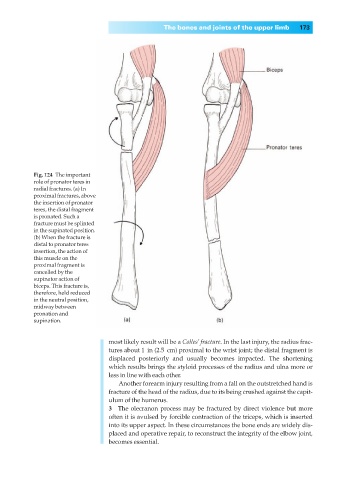
Fig. 124◊The important
role of pronator teres in
radial fractures. (a) In
proximal fractures, above
the insertion of pronator
teres, the distal fragment
is pronated. Such a
fracture must be splinted
in the supinated position.
(b) When the fracture is
distal to pronator teres
insertion, the action of
this muscle on the
proximal fragment is
cancelled by the
supinator action of
biceps. This fracture is,
therefore, held reduced
in the neutral position,
midway between
pronation and
supination.
most likely result will be a Colles’ fracture. In the last injury, the radius frac-
tures about 1 | in (2.5 | cm) proximal to the wrist joint; the distal fragment is
displaced posteriorly and usually becomes impacted. The shortening
which results brings the styloid processes of the radius and ulna more or
less in line with each other.
Another forearm injury resulting from a fall on the outstretched hand is
fracture of the head of the radius, due to its being crushed against the capit-
ulum of the humerus.
3◊◊The olecranon process may be fractured by direct violence but more
often it is avulsed by forcible contraction of the triceps, which is inserted
into its upper aspect. In these circumstances the bone ends are widely dis-
placed and operative repair, to reconstruct the integrity of the elbow joint,
becomes essential.